Deep learning for the fully automated segmentation of the inner ear on MRI
- PMID: 33536451
- PMCID: PMC7858625
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-82289-y
Deep learning for the fully automated segmentation of the inner ear on MRI
Abstract
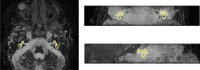
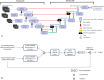
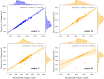
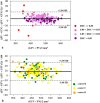
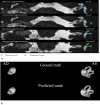
Segmentation of anatomical structures is valuable in a variety of tasks, including 3D visualization, surgical planning, and quantitative image analysis. Manual segmentation is time-consuming and deals with intra and inter-observer variability. To develop a deep-learning approach for the fully automated segmentation of the inner ear in MRI, a 3D U-net was trained on 944 MRI scans with manually segmented inner ears as reference standard. The model was validated on an independent, multicentric dataset consisting of 177 MRI scans from three different centers. The model was also evaluated on a clinical validation set containing eight MRI scans with severe changes in the morphology of the labyrinth. The 3D U-net model showed precise Dice Similarity Coefficient scores (mean DSC-0.8790) with a high True Positive Rate (91.5%) and low False Discovery Rate and False Negative Rates (14.8% and 8.49% respectively) across images from three different centers. The model proved to perform well with a DSC of 0.8768 on the clinical validation dataset. The proposed auto-segmentation model is equivalent to human readers and is a reliable, consistent, and efficient method for inner ear segmentation, which can be used in a variety of clinical applications such as surgical planning and quantitative image analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
M.F.J.A van der Lubbe, Marc van Hoof, Sergey Primakov, A.A. Postma, T.D. Bruintjes, M.A.L. Bilderbeek , Hammer Sebastiaan, P.F.M. Dammeijer, V. van Rompaey and R. van de Berg have no competing interests Fadila Zerka, Akshayaa Vaidyanathan, and Benjamin Miraglio are salaried employees of Oncoradiomics SA. Dr Philippe Lambin reports, within and outside the submitted work, grants/sponsored research agreements from Varian medical, Oncoradiomics, ptTheragnostic/DNAmito, Health Innovation Ventures. He received an advisor/presenter fee and/or reimbursement of travel costs/external grant writing fee and/or in kind manpower contribution from Oncoradiomics, BHV, Merck, Varian, Elekta, ptTheragnostic and Convert pharmaceuticals. Dr Lambin has shares in the company Oncoradiomics SA, Convert pharmaceuticals SA and The Medical Cloud Company SPRL and is co-inventor of two issued patents with royalties on radiomics (PCT/NL2014/050248, PCT/NL2014/050728) licensed to Oncoradiomics and one issue patent on mtDNA (PCT/EP2014/059089) licensed to ptTheragnostic/DNAmito, three non-patented invention (softwares) licensed to ptTheragnostic/DNAmito, Oncoradiomics and Health Innovation Ventures and three non-issues, non licensed patents on Deep Learning-Radiomics and LSRT (N2024482, N2024889, N2024889. Ralph T.H. Leijenaar has shares in the company Oncoradiomics and is co-inventor of an issued patent with royalties on radiomics (PCT/NL2014/050728) licensed to Oncoradiomics. Sean Walsh and Wim Vos have shares in the company Oncoradiomics. Henry C. Woodruff has minority shares in the company Oncoradiomics.
Figures


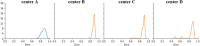

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

