Combined analysis of miR-200 family and its significance for breast cancer
- PMID: 33536459
- PMCID: PMC7859396
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-82286-1
Combined analysis of miR-200 family and its significance for breast cancer
Abstract
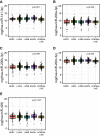
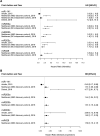
While the molecular functions of miR-200 family have been deeply investigated, a role for these miRNAs as breast cancer biomarkers remains largely unexplored. In the attempt to clarify this, we profiled the miR-200 family members expression in a large cohort of breast cancer cases with a long follow-up (H-CSS cohort) and in TCGA-BRCA cohort. Overall, miR-200 family was found upregulated in breast tumors with respect to normal breast tissues while downregulated in more aggressive breast cancer molecular subtypes (i.e. Luminal B, HER2 and triple negative), consistently with their function as repressors of the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT). In particular miR-141-3p was found differentially expressed in breast cancer molecular subtypes in both H-CSS and TCGA-BRCA cohorts, and the combined analysis of all miR-200 family members demonstrated a slight predictive accuracy on H-CSS cancer specific survival at 12 years (survival c-statistic: 0.646; 95%CI 0.538-0.754).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

