Upregulation and stabilization of senescence marker protein-30 by epigallocatechin gallate against tert-butyl hydroperoxide-induced liver injury in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 33536712
- PMCID: PMC7844653
- DOI: 10.3164/jcbn.20-119
Upregulation and stabilization of senescence marker protein-30 by epigallocatechin gallate against tert-butyl hydroperoxide-induced liver injury in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
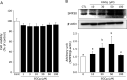
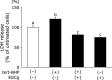
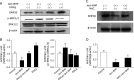
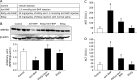
Senescence marker protein-30 (SMP30), a novel ageing marker, suppresses oxidative stress in the liver. However, studies on phytochemical-mediated regulation of SMP30 expression are lacking. Here, we showed that epigallocatechin gallate (EGCg), a polyphenol abundant in green tea, positively regulates SMP30 expression in the rat hepatoma-derived Fao cells. EGCg maintained SMP30 expression even in the presence of cycloheximide, a protein synthesis inhibitor. Furthermore, treatment of cells with tert-butyl hydroperoxide (tert-BHP), an oxidative promoter, decreased SMP30 expression and ERK1/2 phosphorylation, while EGCg treatment inhibited these effects. Male mice (7-week-old) were divided into 4 groups-Control (saline), tert-BHP (1.5 mmol/kg tert-BHP), EGCg + tert-BHP (30 mg/kg/day of EGCg and 1.5 mmol/kg tert-BHP), and EGCg (30 mg/kg/day). After oral EGCg administration for 6 consecutive days, EGCg + tert-BHP group mice were administered tert-BHP. The tert-BHP-administered mice showed decreased SMP30 expression in the liver and increased aspartate aminotransferase and alanine transaminase (hepatic injury marker enzymes) activities; however, EGCg treatment attenuated these changes. Thus, EGCg-induced SMP30 upregulation may alleviate tert-BHP-induced liver injury. The findings of this study offer new perspectives of the anti-ageing properties of EGCg.
Keywords: epigallocatechin gallate; senescence marker protein-30; tert-BHP-induced liver injury.
Copyright © 2021 JCBN.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Protective Effect of Epigallocatechin-3-gallate against Hepatic Oxidative Stress Induced by tert-Butyl Hhydroperoxide in Yellow-Feathered Broilers.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Sep 24;13(10):1153. doi: 10.3390/antiox13101153. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39456408 Free PMC article.
-
DHA sensitizes FaO cells to tert-BHP-induced oxidative effects. Protective role of EGCG.Food Chem Toxicol. 2013 Dec;62:750-7. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2013.10.013. Epub 2013 Oct 16. Food Chem Toxicol. 2013. PMID: 24140970
-
Resveratrol Upregulates Senescence Marker Protein 30 by Activating AMPK/Sirt1-Foxo1 Signals and Attenuating H2O2-Induced Damage in FAO Rat Liver Cells.J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 2023;69(5):388-393. doi: 10.3177/jnsv.69.388. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 2023. PMID: 37940580
-
Pathobiological Mechanisms of Endothelial Dysfunction Induced by tert-Butyl Hydroperoxide via Apoptosis, Necrosis and Senescence in a Rat Model.Int J Med Sci. 2020 Feb 4;17(3):368-382. doi: 10.7150/ijms.40255. eCollection 2020. Int J Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32132872 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary pretreatment with green tea polyphenol, (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate reduces the bioavailability and hepatotoxicity of subsequent oral bolus doses of (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate.Food Chem Toxicol. 2015 Feb;76:103-8. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2014.12.009. Epub 2014 Dec 17. Food Chem Toxicol. 2015. PMID: 25528115 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hernandez-Segura A, Nehme J, Demaria M. Hallmarks of cellular senescence. Trends Cell Biol 2018; 28: 436–453. - PubMed
-
- vB Hjelmborg J, Iachine I, Skytthe A, et al. Genetic influence on human lifespan and longevity. Hum Genet 2006; 119: 312–321. - PubMed
-
- Lakatta EG, Levy D. Arterial and cardiac aging: major shareholders in cardiovascular disease enterprises: Part I: aging arteries: a “set up” for vascular disease. Circulation 2003; 107: 139–146. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

