IL-15 Upregulates Telomerase Expression and Potently Increases Proliferative Capacity of NK, NKT-Like, and CD8 T Cells
- PMID: 33537030
- PMCID: PMC7848219
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.594620
IL-15 Upregulates Telomerase Expression and Potently Increases Proliferative Capacity of NK, NKT-Like, and CD8 T Cells
Abstract
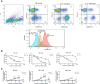
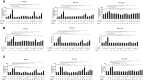
Interleukin-15 (IL-15) is a cytokine that has been shown to expand CD8 T cell and natural killer (NK) cell populations, and therefore has potential for potentiating adoptive immune cell therapy for cancer. Previously, IL-15 has been shown to induce proliferation of CD8 memory T cells through activation of telomerase. Here, we investigated whether telomerase is also activated during the IL-15 mediated proliferation of NK and NKT-like (CD56+CD3+) cells. We also examined the extent that each of the three signaling pathways known to be stimulated by IL-2/IL-15 (JAK-STAT, PI3K-AKT Ras-RAF/MAPK) were activated and involved in the telomerase expression in the three cell types NK, NKT, or CD8 T cells. To assess cell proliferation and doubling, peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) or isolated NK, NKT-like or CD8 T cells were incubated with varying concentrations of IL-15 or IL-2 for 7 days. CD8 T, NK, and NKT cell expansion was determined by fluorophore-conjugated antibody staining and flow cytometry. Cell doubling was investigated using carboxyfluorescein-succinimidyl-ester (CFSE). Telomerase expression was investigated by staining cells with anti-telomerase reverse transcriptase (anti-TERT). Telomerase activity in CD56+ and CD8 T cells was also measured via Telomerase Repeat Amplification Protocol (TRAP). Analysis of cellular expansion, proliferation and TERT expression concluded that IL-15 increased cellular growth of NK, NKT, and CD8 T cells more effectively than IL-2 using low or high doses. IL-15, increased TERT expression in NK and NKT cells by up to 2.5 fold, the same increase seen in CD8 T cells. IL-2 had effects on TERT expression only at high doses (100-1000 ng/ml). Proteome profiling identified that IL-15 activated selected signaling proteins in the three pathways (JAK-STAT, PI3K-AKT, Ras-MAPK) known to mediate IL-2/IL-15 signaling, more strongly than IL-2. Evaluation by signaling pathway inhibitors revealed that JAK/STAT and PI3K/AKT pathways are important in IL-15's ability to upregulate TERT expression in NK and NKT cells, whereas all three pathways were involved in CD8 T cell TERT expression. In conclusion, this study shows that IL-15 potently stimulates TERT upregulation in NK and NKT cells in addition to CD8 T cells and is therefore a valuable tool for adoptive cell therapies.
Keywords: adoptive cell therapy; cell-signaling; interleukin-15; interleukin-2; telomerase.
Copyright © 2021 Watkinson, Nayar, Rani, Sakellariou, Elhage, Papaevangelou, Dasgupta and Galustian.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
IL-15R alpha-IgG1-Fc enhances IL-2 and IL-15 anti-tumor action through NK and CD8+ T cells proliferation and activation.J Mol Cell Biol. 2010 Aug;2(4):217-22. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjq012. J Mol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20671116
-
Ex vivo expansion of CD8+CD56+ and CD8+CD56- natural killer T cells specific for MUC1 mucin.Cancer Res. 2004 Feb 1;64(3):1171-80. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.can-3254-2. Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 14871854
-
Characterization of natural killer and natural killer-like T cells derived from ex vivo expanded and activated cord blood mononuclear cells: implications for adoptive cellular immunotherapy.Exp Hematol. 2009 Oct;37(10):1216-29. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2009.07.009. Epub 2009 Jul 26. Exp Hematol. 2009. PMID: 19638292
-
Antitumor immunity produced by the liver Kupffer cells, NK cells, NKT cells, and CD8 CD122 T cells.Clin Dev Immunol. 2011;2011:868345. doi: 10.1155/2011/868345. Epub 2011 Nov 29. Clin Dev Immunol. 2011. PMID: 22190974 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IL-15: targeting CD8+ T cells for immunotherapy.Cytotherapy. 2005;7(1):23-35. doi: 10.1080/14653240510018037. Cytotherapy. 2005. PMID: 16040381 Review.
Cited by
-
Myokines May Be the Answer to the Beneficial Immunomodulation of Tailored Exercise-A Narrative Review.Biomolecules. 2024 Sep 25;14(10):1205. doi: 10.3390/biom14101205. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39456138 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of Telomere Length in T Lymphocytes, B Lymphocytes, NK Cells and Monocytes with Different Forms of Age-Related Macular Degeneration.Biomedicines. 2024 Aug 19;12(8):1893. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12081893. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39200358 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in CAR-T cells therapy for colorectal cancer.Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 27;13:904137. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.904137. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36238297 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytotopic (Cyto-) IL-15 as a New Immunotherapy for Prostate Cancer: Recombinant Production in Escherichia coli and Purification.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Oct 27;8:755764. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.755764. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34778376 Free PMC article.
-
The role of interleukin-15 in the development and treatment of hematological malignancies.Front Immunol. 2023 Apr 20;14:1141208. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1141208. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37153603 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Conlon KC, Potter EL, Pittaluga S, Lee C-CR, Miljkovic MD, Fleisher TA, et al. IL15 by Continuous Intravenous Infusion to Adult Patients with Solid Tumors in a Phase I Trial Induced Dramatic NK-Cell Subset Expansion. J Clin Cancer Res (2019) 25(16):4945–54. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-3468 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

