R848 Is Involved in the Antibacterial Immune Response of Golden Pompano (Trachinotus ovatus) Through TLR7/8-MyD88-NF-κB-Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 33537035
- PMCID: PMC7848160
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.617522
R848 Is Involved in the Antibacterial Immune Response of Golden Pompano (Trachinotus ovatus) Through TLR7/8-MyD88-NF-κB-Signaling Pathway
Abstract
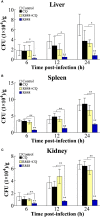
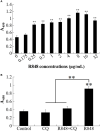
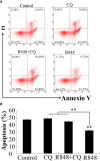
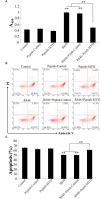
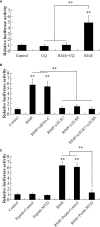
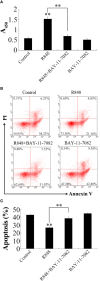
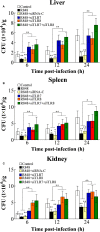
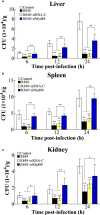
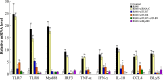
R848 is an imidazoquinoline compound that is a specific activator of toll-like receptor (TLR) 7/8 and is often used in immunological research in mammals and teleosts. However, the immune responses initiated by R848 through the TLR7/8 pathway in response to bacterial infection remain largely unexplored in teleosts. In the current study, we investigated the antibacterial response and the participating signaling pathway initiated by R848 in golden pompano (Trachinotus ovatus). We found that R848 could stimulate the proliferation of head kidney lymphocytes (HKLs) in a dose-dependent manner, enhance the survival rate of HKLs, and inhibit the replication of bacteria in vivo. However, these effects induced by R848 were significantly reduced when chloroquine (CQ) was used to blocked endosomal acidification. Additionally, an in vivo study showed that R848 strengthened the antibacterial immunity of fish through a TLR7/8 and Myd88-dependent signaling pathway. A cellular experiment showed that Pepinh-MYD (a Myd88 inhibitor) significantly reduced the R848-mediated proliferation and survival of HKLs. Luciferase activity analysis showed that R848 enhanced the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) activity, whereas this activity was reduced when CQ and Pepinh-MYD were present. Additionally, when an NF-κB inhibitor was present, the R848-mediated pro-proliferative and pro-survival effects on HKLs were significantly diminished. An in vivo study showed that knockdown of TLR7, TLR8, and Myd88 expression in golden pompano via siRNA following injection of R848 resulted in increased bacterial dissemination and colonization in fish tissues compared to that of fish injection of R848 alone, suggesting that R848-induced antibacterial immunity was significantly reduced. In conclusion, these results indicate that R848 plays an essential role in the antibacterial immunity of golden pompano via the TLR7/8-Myd88-NF-κB- signaling pathway.
Keywords: Myd88; NF-κB; R848; TLR7/8; antibacterial immune response.
Copyright © 2021 Zhou, Chen, Cao, Li, Long, Wu, Zhang and Sun.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

