A Method to Minimise the Impact of ECG Marker Inaccuracies on the Spatial QRS-T angle: Evaluation on 1,512 Manually Annotated ECGs
- PMID: 33537064
- PMCID: PMC7762839
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bspc.2020.102305
A Method to Minimise the Impact of ECG Marker Inaccuracies on the Spatial QRS-T angle: Evaluation on 1,512 Manually Annotated ECGs
Abstract
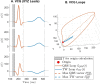
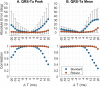
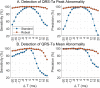
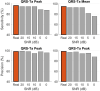
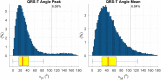
The spatial QRS-T angle (QRS-Ta) derived from the vectorcardiogram (VCG) is a strong risk predictor for ventricular arrhythmia and sudden cardiac death with potential use for mass screening. Accurate QRS-Ta estimation in the presence of ECG delineation errors is crucial for its deployment as a prognostic test. Our study assessed the effect of inaccurate QRS and T-wave marker placement on QRS-Ta estimation and proposes a robust method for its calculation. Reference QRS-Ta measurements were derived from 1,512 VCGs manually annotated by three expert reviewers. We systematically changed onset and offset timings of QRS and T-wave markers to simulate inaccurate placement. The QRS-Ta was recalculated using a standard approach and our proposed algorithm, which limits the impact of VCG marker inaccuracies by defining the vector origin as an interval preceding QRS-onset and redefines the beginning and end of QRS and T-wave loops. Using the standard approach, mean absolute errors (MAE) in peak QRS-Ta were >40% and sensitivity and precision in the detection of abnormality (>105°) were <80% and <65% respectively, when QRS-onset was delayed or QRS-offset anticipated >15 ms. Using our proposed algorithm, MAE for peak QRS-Ta were reduced to <4% and sensitivity and precision of abnormality were >94% for inaccuracies up to ±15 ms. Similar results were obtained for mean QRS-Ta. In conclusion, inaccuracies of QRS and T-wave markers can significantly influence the QRS-Ta. Our proposed algorithm provides robust QRS-Ta measurements in the presence of inaccurate VCG annotation, enabling its use in large datasets.
Keywords: Automatic analysis; Electrocardiogram; Population distribution; Spatial QRS-T angle; Vectorcardiogram.
© 2020 The Author(s).
Figures

References
-
- Waks J.W., Sitlani C.M., Soliman E.Z., Kabir M., Ghafoori E., Biggs M.L. Global electric heterogeneity risk score for prediction of sudden cardiac death in the general population: the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) and Cardiovascular Health (CHS) Studies. Circulation. 2016;133(June (23)):2222–2234. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.021306. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
