Laser nanobubbles induce immunogenic cell death in breast cancer
- PMID: 33538275
- PMCID: PMC8710258
- DOI: 10.1039/d0nr06587k
Laser nanobubbles induce immunogenic cell death in breast cancer
Abstract
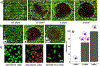
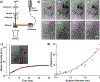
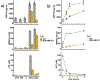
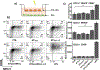
Recent advances in immunotherapy have highlighted a need for therapeutics that initiate immunogenic cell death in tumors to stimulate the body's immune response to cancer. This study examines whether laser-generated bubbles surrounding nanoparticles ("nanobubbles") induce an immunogenic response for cancer treatment. A single nanosecond laser pulse at 1064 nm generates micron-sized bubbles surrounding gold nanorods in the cytoplasm of breast cancer cells. Cell death occurred in cells treated with nanorods and irradiated, but not in cells with irradiation treatment alone. Cells treated with nanorods and irradiation had increased damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), including increased expression of chaperone proteins human high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1), adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and heat shock protein 70 (HSP70). This enhanced expression of DAMPs led to the activation of dendritic cells. Overall, this treatment approach is a rapid and highly specific method to eradicate tumor cells with simultaneous immunogenic cell death signaling, showing potential as a combination strategy for immunotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Hodi FS, O’Day SJ, McDermott DF, Weber RW, Sosman JA, Haanen JB, Gonzalez R, Robert C, Schadendorf D, Hassel JC, Akerley W, van den Eertwegh AJM, Lutzky J, Lorigan P, Vaubel JM, Linette GP, Hogg D, Ottensmeier CH, Lebbé C, Peschel C, Quirt I, Clark JI, Wolchok JD, Weber JS, Tian J, Yellin MJ, Nichol GM, Hoos A. and Urba WJ, N. Engl. J. Med, 2010, 363, 711–723. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wei SC, Duffy CR and Allison JP, Cancer Discovery, 2018, 8, 1069–1086. - PubMed
-
- Sharma P. and Allison JP, Science, 2015, 348, 56–61. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

