Analytical 2-Dimensional Model of Nonpolar and Ionic Solvation in Water
- PMID: 33539097
- PMCID: PMC7958497
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.0c10329
Analytical 2-Dimensional Model of Nonpolar and Ionic Solvation in Water
Abstract
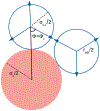
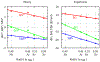
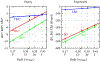
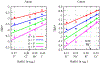
A goal in computational chemistry is computing hydration free energies of nonpolar and charged solutes accurately, but with much greater computational speeds than in today's explicit-water simulations. Here, we take one step in that direction: a simple model of solvating waters that is analytical and thus essentially instantaneous to compute. Each water molecule is a 2-dimensional dipolar hydrogen-bonding disk that interacts around small circular solutes with different nonpolar and charge interactions. The model gives good qualitative agreement with experiments. As a function of the solute radius, it gives the solvation free energy, enthalpy and entropy as a function of temperature for the inert gas series Ne, Ar, Kr, and Xe. For anions and cations, it captures relatively well the trends versus ion radius. This approach should be readily generalizable to three dimensions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures










References
-
- Hermann RB Theory of Hydrophobic Bonding. II. The Correlation of Hydrocarbon Solubility in Water with Solvent Cavity Surface Area. J. Phys. Chem 1972, 76, 2754–2759.
-
- Urbič T; Vlachy V; Kalyuzhnyi YV; Southall NT; Dill KA A Two-Dimensional Model of Water: Solvation of Nonpolar Solutes. J. Chem. Phys 2002, 116, 723–729.
-
- Urbič T; Vlachy V; Kalyuzhnyi YV; Dill KA Orientation-Dependent Integral Equation Theory for a Two-Dimensional Model of Water. J. Chem. Phys 2003, 118, 5516–5525.
-
- Urbic T; Vlachy V; Kalyuzhnyi YV; Dill KA Theory for the Solvation of Nonpolar Solutes in Water. J. Chem. Phys 2007, 127, 174505. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

