Endothelial Cell Receptors in Tissue Lipid Uptake and Metabolism
- PMID: 33539224
- PMCID: PMC7959116
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.318003
Endothelial Cell Receptors in Tissue Lipid Uptake and Metabolism
Abstract
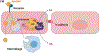
Lipid uptake and metabolism are central to the function of organs such as heart, skeletal muscle, and adipose tissue. Although most heart energy derives from fatty acids (FAs), excess lipid accumulation can cause cardiomyopathy. Similarly, high delivery of cholesterol can initiate coronary artery atherosclerosis. Hearts and arteries-unlike liver and adrenals-have nonfenestrated capillaries and lipid accumulation in both health and disease requires lipid movement from the circulation across the endothelial barrier. This review summarizes recent in vitro and in vivo findings on the importance of endothelial cell receptors and uptake pathways in regulating FAs and cholesterol uptake in normal physiology and cardiovascular disease. We highlight clinical and experimental data on the roles of ECs in lipid supply to tissues, heart, and arterial wall in particular, and how this affects organ metabolism and function. Models of FA uptake into ECs suggest that receptor-mediated uptake predominates at low FA concentrations, such as during fasting, whereas FA uptake during lipolysis of chylomicrons may involve paracellular movement. Similarly, in the setting of an intact arterial endothelial layer, recent and historic data support a role for receptor-mediated processes in the movement of lipoproteins into the subarterial space. We conclude with thoughts on the need to better understand endothelial lipid transfer for fuller comprehension of the pathophysiology of hyperlipidemia, and lipotoxic diseases such as some forms of cardiomyopathy and atherosclerosis.
Keywords: cardiomyopathy; chylomicrons; fatty acids; lipoprotein; triglyceride.
Figures


References
-
- Duncan JG, Bharadwaj KG, Fong JL, Mitra R, Sambandam N, Courtois MR, Lavine KJ, Goldberg IJ and Kelly DP. Rescue of cardiomyopathy in peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha transgenic mice by deletion of lipoprotein lipase identifies sources of cardiac lipids and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha activators. Circulation. 2010;121:426–35. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yang J, Sambandam N, Han X, Gross RW, Courtois M, Kovacs A, Febbraio M, Finck BN and Kelly DP. CD36 deficiency rescues lipotoxic cardiomyopathy. Circ Res. 2007;100:1208–17. - PubMed
-
- Glatz JFC, Zuurbier CJ and Larsen TS. Targeting metabolic pathways to treat cardiovascular diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2020;1866:165879. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

