Swab pooling: A new method for large-scale RT-qPCR screening of SARS-CoV-2 avoiding sample dilution
- PMID: 33539474
- PMCID: PMC7861376
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0246544
Swab pooling: A new method for large-scale RT-qPCR screening of SARS-CoV-2 avoiding sample dilution
Abstract
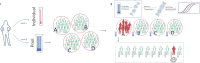
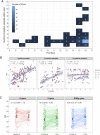
To minimize sample dilution effect on SARS-CoV-2 pool testing, we assessed analytical and diagnostic performance of a new methodology, namely swab pooling. In this method, swabs are pooled at the time of collection, as opposed to pooling of equal volumes from individually collected samples. Paired analysis of pooled and individual samples from 613 patients revealed 94 positive individuals. Having individual testing as reference, no false-positives or false-negatives were observed for swab pooling. In additional 18,922 patients screened with swab pooling (1,344 pools), mean Cq differences between individual and pool samples ranged from 0.1 (Cr.I. -0.98 to 1.17) to 2.09 (Cr.I. 1.24 to 2.94). Overall, 19,535 asymptomatic patients were screened using 4,400 RT-qPCR assays. This corresponds to an increase of 4.4 times in laboratory capacity and a reduction of 77% in required tests. Therefore, swab pooling represents a major alternative for reliable and large-scale screening of SARS-CoV-2 in low prevalence populations.
Conflict of interest statement
APC, GNFC, AFR, DRB, DCB, LEY and LFVO from BiomeHub are currently full-time employees of this company. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials. All other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Lee S, Kim T, Lee E, Lee C, Kim H, Rhee H, et al. Clinical Course and Molecular Viral Shedding Among Asymptomatic and Symptomatic Patients With SARS-CoV-2 Infection in a Community Treatment Center in the Republic of Korea. Jama Intern Med. 2020;180 10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.3862 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

