Inclusion of Safety-Related Issues in Economic Evaluations for Seasonal Influenza Vaccines: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 33540633
- PMCID: PMC7913116
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines9020111
Inclusion of Safety-Related Issues in Economic Evaluations for Seasonal Influenza Vaccines: A Systematic Review
Abstract
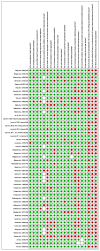
(1) Background: Vaccines for seasonal influenza are a good preventive and cost-effective strategy. However, it is unknown if and how these economic evaluations include the adverse events following immunization (AEFI), and what the impact of such inclusion is on the health economic outcomes. (2) Methods: We searched the literature, up to January 2020, to identify economic evaluations of seasonal influenza vaccines that considered AEFIs. The review protocol was published in PROSPERO (CDR42017058523). (3) Results: A total of 52 economic evaluations considered AEFI-related parameters in their analyses, reflecting 16% of the economic evaluations on seasonal influenza vaccines in the initial study selection. Most studies used the societal perspective (64%) and evaluated vaccination of children (37%). Where considered, studies included direct medical costs of AEFIs (90%), indirect costs (27%), and disutilities/quality-adjusted life years loss due to AEFIs (37%). The majority of these studies accounted for the effects of the costs of AEFI on cost-effectiveness for Guillain-Barré syndrome. In those papers allowing cost share estimation, direct medical cost of AFEIs was less than 2% of total direct costs. (4) Conclusions: Although the overall impact of AEFIs on the cost-effectiveness outcomes was found to be low, we urge their inclusion in economic evaluations of seasonal influenza vaccines to reflect comprehensive reports for the decision makers and end-users of the vaccination strategies.
Keywords: adverse events following immunization; economic evaluations; seasonal influenza vaccines.
Conflict of interest statement
This study was not funded. T.F. and E.P.v.P. report no conflicts of interest. The appointment of P.T.d.B. was partly supported by grants of different pharmaceutical companies, including companies involved in the subject matter of this study. M.J.P. reports grants and personal fees from various pharmaceutical industries, all outside the submitted work. M.J.P. holds stocks in Health-Ecore and Pharmacoeconomics Advice Groningen (PAG Ltd.) and is an advisor to Asc Academics.
Figures


References
-
- WHO Influenza (Seasonal) [(accessed on 16 January 2019)]; Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/influenza-(seasonal)
-
- ECDC Seasonal Influenza Vaccines. [(accessed on 16 January 2019)]; Available online: http://ecdc.europa.eu/en/seasonal-influenza/prevention-and-control/seaso....
-
- ECDC Types of Seasonal Influenza Vaccine. [(accessed on 16 January 2019)]; Available online: http://ecdc.europa.eu/en/seasonal-influenza/prevention-and-control/vacci....
-
- World Health Organization Types of Seasonal Influenza Vaccine. [(accessed on 5 July 2019)]; Available online: http://www.euro.who.int/en/health-topics/communicable-diseases/influenza....
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

