Mitochondrial Homeostasis Mediates Lipotoxicity in the Failing Myocardium
- PMID: 33540894
- PMCID: PMC7867320
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22031498
Mitochondrial Homeostasis Mediates Lipotoxicity in the Failing Myocardium
Abstract
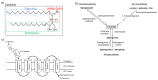
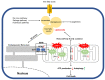
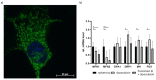
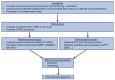
Heart failure remains the most common cause of death in the industrialized world. In spite of new therapeutic interventions that are constantly being developed, it is still not possible to completely protect against heart failure development and progression. This shows how much more research is necessary to understand the underlying mechanisms of this process. In this review, we give a detailed overview of the contribution of impaired mitochondrial dynamics and energy homeostasis during heart failure progression. In particular, we focus on the regulation of fatty acid metabolism and the effects of fatty acid accumulation on mitochondrial structural and functional homeostasis.
Keywords: heart failure; lipotoxicity; metabolism; mitochondrial homeostasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Benjamin E.J., Muntner P., Alonso A., Bittencourt M.S., Callaway C.W., Carson A.P., Chamberlain A.M., Chang A.R., Cheng S., Das S.R., et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2019 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2019;139:e56–e528. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000659. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Scally C., Rudd A., Mezincescu A., Wilson H., Srivanasan J., Horgan G., Broadhurst P., Newby D.E., Henning A., Dawson D.K. Persistent Long-Term Structural, Functional, and Metabolic Changes After Stress-Induced (Takotsubo) Cardiomyopathy. Circulation. 2018;137:1039–1048. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.031841. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Marcinkiewicz-Siemion M., Ciborowski M., Ptaszynska-Kopczynska K., Szpakowicz A., Lisowska A., Jasiewicz M., Waszkiewicz E., Kretowski A., Musial W.J., Kaminski K.A. LC-MS-based serum fingerprinting reveals significant dysregulation of phospholipids in chronic heart failure. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018;154:354–363. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2018.03.027. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

