Lipid Nanoparticles as Delivery Systems for RNA-Based Vaccines
- PMID: 33540942
- PMCID: PMC7913163
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13020206
Lipid Nanoparticles as Delivery Systems for RNA-Based Vaccines
Abstract
There has been increased interest in the development of RNA-based vaccines for protection against various infectious diseases and also for cancer immunotherapies. Rapid and cost-effective manufacturing methods in addition to potent immune responses observed in preclinical and clinical studies have made mRNA-based vaccines promising alternatives to conventional vaccine technologies. However, efficient delivery of these vaccines requires that the mRNA be protected against extracellular degradation. Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) have been extensively studied as non-viral vectors for the delivery of mRNA to target cells because of their relatively easy and scalable manufacturing processes. This review highlights key advances in the development of LNPs and reviews the application of mRNA-based vaccines formulated in LNPs for use against infectious diseases and cancer.
Keywords: adjuvant; cancer immunotherapy; cationic lipids; delivery system; lipid nanoparticles; mRNA; nanotechnology; nucleic acid; vaccines.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
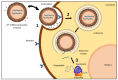
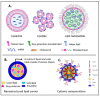
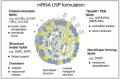
References
-
- Brito L.A., Kommareddy S., Maione D., Uematsu Y., Giovani C., Scorza F.B., Otten G.R., Yu D., Mandl C.W., Mason P.W. Advances in Genetics. Volume 89. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2015. Self-amplifying mRNA vaccines; pp. 179–233. - PubMed
-
- Pascolo S. Toll-Like Receptors (TLRs) and Innate Immunity. Springer; Berlin, Germany: 2008. Vaccination with messenger RNA (mRNA) pp. 221–235. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

