Immunogenicity and safety of a quadrivalent meningococcal tetanus toxoid-conjugate vaccine (MenACYW-TT) vs. a licensed quadrivalent meningococcal tetanus toxoid-conjugate vaccine in meningococcal vaccine-naïve and meningococcal C conjugate vaccine-primed toddlers: a phase III randomised study
- PMID: 33541457
- PMCID: PMC8060839
- DOI: 10.1017/S0950268821000261
Immunogenicity and safety of a quadrivalent meningococcal tetanus toxoid-conjugate vaccine (MenACYW-TT) vs. a licensed quadrivalent meningococcal tetanus toxoid-conjugate vaccine in meningococcal vaccine-naïve and meningococcal C conjugate vaccine-primed toddlers: a phase III randomised study
Abstract
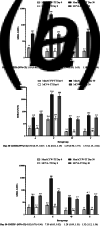
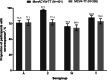
Vaccination remains the best strategy to reduce invasive meningococcal disease. This study evaluated an investigational tetanus toxoid-conjugate quadrivalent meningococcal vaccine (MenACYW-TT) vs. a licensed tetanus toxoid-conjugate quadrivalent meningococcal vaccine (MCV4-TT) (NCT02955797). Healthy toddlers aged 12-23 months were included if they were either meningococcal vaccine-naïve or MenC conjugate (MCC) vaccine-primed (≥1 dose of MCC prior to 12 months of age). Vaccine-naïve participants were randomised 1:1 to either MenACYW-TT (n = 306) or MCV4-TT (n = 306). MCC-primed participants were randomised 2:1 to MenACYW-TT (n = 203) or MCV4-TT (n = 103). Antibody titres against each of the four meningococcal serogroups were measured by serum bactericidal antibody assay using the human complement. The co-primary objectives of this study were to demonstrate the non-inferiority of MenACYW-TT to MCV4-TT in terms of seroprotection (titres ≥1:8) at Day 30 in both vaccine-naïve and all participants (vaccine-naïve and MCC-primed groups pooled). The immune response for all four serogroups to MenACYW-TT was non-inferior to MCV4-TT in vaccine-naïve participants (seroprotection: range 83.6-99.3% and 81.4-91.6%, respectively) and all participants (seroprotection: range 83.6-99.3% and 81.4-98.0%, respectively). The safety profiles of both vaccines were comparable. MenACYW-TT was well-tolerated and demonstrated non-inferior immunogenicity when administered to MCC vaccine-primed and vaccine-naïve toddlers.
Keywords: IMD; MenACYW-TT; quadrivalent meningococcal vaccine; toddlers.
Conflict of interest statement
FM-T has received honoraria from GSK, Pfizer, Sanofi Pasteur, MSD, Seqirus and Janssen for taking part in advisory boards and expert meetings, and for acting as speaker in congresses outside the scope of the submitted work. FM-T has also acted as principal investigator in RCTs of the above-mentioned companies as well as Ablynx, Regeneron, Roche, Abbott, Novavax and MedImmune, with honoraria paid to his institution. FM-T research activities received support from the Instituto de Salud Carlos III (Proyecto de Investigación en Salud, Acción Estratégica en Salud): Fondo de Investigación Sanitaria (FIS; PI070069/PI1000540/PI1601569/PI1901090) del plan nacional de I + D + I and ‘fondos FEDER’ and 2016-PG071 Consolidación e Estructuración REDES 2016GI-1344 G3VIP (Grupo Gallego de Genética Vacunas Infecciones y Pediatría, ED341D R2016/021). AF, BS, GM, RS, TA and CDG, have no conflicts to declare. TV, received funding to his institute from Sanofi Pasteur for the conduct of this study, has received honoraria from Sanofi Pasteur for advisory boards. DvdV, SB'C, DN, EJ, MSD are employees of Sanofi Pasteur.
Figures

References
-
- Martinón-Torres F (2016) Deciphering the burden of meningococcal disease: conventional and under-recognized elements. Journal of Adolescent Health 59(suppl. 2), S12–S20. - PubMed
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control, Invasive meningococcal disease: Annual Epidemiological Report for 2017. Available at https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/sites/default/files/documents/AER_for_2017-in....
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

