Therapeutic Targeting of Nemo-like Kinase in Primary and Acquired Endocrine-resistant Breast Cancer
- PMID: 33542078
- PMCID: PMC8653766
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-2961
Therapeutic Targeting of Nemo-like Kinase in Primary and Acquired Endocrine-resistant Breast Cancer
Abstract
Purpose: Endocrine resistance remains a major clinical challenge in estrogen receptor (ER)-positive breast cancer. Despite the encouraging results from clinical trials for the drugs targeting known survival signaling, relapse is still inevitable. There is an unmet need to discover new drug targets in the unknown escape pathways. Here, we report Nemo-like kinase (NLK) as a new actionable kinase target that endows previously uncharacterized survival signaling in endocrine-resistant breast cancer.
Experimental design: The effects of NLK inhibition on the viability of endocrine-resistant breast cancer cell lines were examined by MTS assay. The effect of VX-702 on NLK activity was verified by kinase assay. The modulation of ER and its coactivator, SRC-3, by NLK was examined by immunoprecipitation, kinase assay, luciferase assay, and RNA sequencing. The therapeutic effects of VX-702 and everolimus were tested on cell line- and patient-derived xenograft (PDX) tumor models.
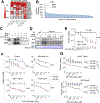
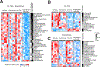
Results: NLK overexpression endows reduced endocrine responsiveness and is associated with worse outcome of patients treated with tamoxifen. Mechanistically, NLK may function, at least in part, via enhancing the phosphorylation of ERα and its key coactivator, SRC-3, to modulate ERα transcriptional activity. Through interrogation of a kinase profiling database, we uncovered and verified a highly selective dual p38/NLK inhibitor, VX-702. Coadministration of VX-702 with the mTOR inhibitor, everolimus, demonstrated a significant therapeutic effect in cell line-derived xenograft and PDX tumor models of acquired or de novo endocrine resistance.
Conclusions: Together, this study reveals the potential of therapeutic modulation of NLK for the management of the endocrine-resistant breast cancers with active NLK signaling.
©2021 American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures




Similar articles
-
AKT Antagonist AZD5363 Influences Estrogen Receptor Function in Endocrine-Resistant Breast Cancer and Synergizes with Fulvestrant (ICI182780) In Vivo.Mol Cancer Ther. 2015 Sep;14(9):2035-48. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-15-0143. Epub 2015 Jun 26. Mol Cancer Ther. 2015. PMID: 26116361
-
Effectiveness and molecular interactions of the clinically active mTORC1 inhibitor everolimus in combination with tamoxifen or letrozole in vitro and in vivo.Breast Cancer Res. 2012 Oct 17;14(5):R132. doi: 10.1186/bcr3330. Breast Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 23075476 Free PMC article.
-
Aurora kinase B is important for antiestrogen resistant cell growth and a potential biomarker for tamoxifen resistant breast cancer.BMC Cancer. 2015 Apr 8;15:239. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1210-4. BMC Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25885472 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing Endocrine Therapy for Hormone Receptor-Positive Advanced Breast Cancer: Cotargeting Signaling Pathways.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2015 Aug 6;107(10):djv212. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djv212. Print 2015 Oct. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2015. PMID: 26251289 Review.
-
Treatment algorithms for hormone receptor-positive advanced breast cancer: going forward in endocrine therapy—overcoming resistance and introducing new agents.Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 2013. doi: 10.14694/EdBook_AM.2013.33.e28. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 2013. PMID: 23714448 Review.
Cited by
-
VX-702 Ameliorates the Severity of Sepsis-Associated Acute Kidney Injury by Downregulating Inflammatory Factors in Macrophages.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Jun 21;17:4037-4054. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S464018. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 38919509 Free PMC article.
-
Strategies for Improving Photodynamic Therapy Through Pharmacological Modulation of the Immediate Early Stress Response.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2451:405-480. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2099-1_20. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35505025 Review.
-
Advances in Research on Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Targets and Therapeutic Agents.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 29;24(17):13381. doi: 10.3390/ijms241713381. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37686185 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of diagnostic markers related to inflammatory response and cellular senescence in endometriosis using machine learning and in vitro experiment.Inflamm Res. 2024 Jul;73(7):1107-1122. doi: 10.1007/s00011-024-01886-5. Epub 2024 May 4. Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 38704432
-
Pharmacological inhibition of PLK1/PRC1 triggers mitotic catastrophe and sensitizes lung cancers to chemotherapy.Cell Death Dis. 2025 May 12;16(1):374. doi: 10.1038/s41419-025-07708-8. Cell Death Dis. 2025. PMID: 40355412 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

