A fine balance between Prpf19 and Exoc7 in achieving degradation of aggregated protein and suppression of cell death in spinocerebellar ataxia type 3
- PMID: 33542212
- PMCID: PMC7862454
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-021-03444-x
A fine balance between Prpf19 and Exoc7 in achieving degradation of aggregated protein and suppression of cell death in spinocerebellar ataxia type 3
Abstract
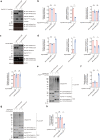
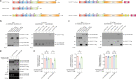
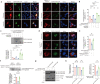
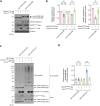
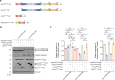
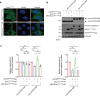
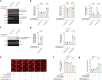
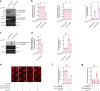
Polyglutamine (polyQ) diseases comprise Huntington's disease and several subtypes of spinocerebellar ataxia, including spinocerebellar ataxia type 3 (SCA3). The genomic expansion of coding CAG trinucleotide sequence in disease genes leads to the production and accumulation of misfolded polyQ domain-containing disease proteins, which cause cellular dysfunction and neuronal death. As one of the principal cellular protein clearance pathways, the activity of the ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS) is tightly regulated to ensure efficient clearance of damaged and toxic proteins. Emerging evidence demonstrates that UPS plays a crucial role in the pathogenesis of polyQ diseases. Ubiquitin (Ub) E3 ligases catalyze the transfer of a Ub tag to label proteins destined for proteasomal clearance. In this study, we identified an E3 ligase, pre-mRNA processing factor 19 (Prpf19/prp19), that modulates expanded ataxin-3 (ATXN3-polyQ), disease protein of SCA3, induced neurodegeneration in both mammalian and Drosophila disease models. We further showed that Prpf19/prp19 promotes poly-ubiquitination and degradation of mutant ATXN3-polyQ protein. Our data further demonstrated the nuclear localization of Prpf19/prp19 is essential for eliciting its modulatory function towards toxic ATXN3-polyQ protein. Intriguingly, we found that exocyst complex component 7 (Exoc7/exo70), a Prpf19/prp19 interacting partner, modulates expanded ATXN3-polyQ protein levels and toxicity in an opposite manner to Prpf19/prp19. Our data suggest that Exoc7/exo70 exerts its ATXN3-polyQ-modifying effect through regulating the E3 ligase function of Prpf19/prp19. In summary, this study allows us to better define the mechanistic role of Exoc7/exo70-regulated Prpf19/prp19-associated protein ubiquitination pathway in SCA3 pathogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inactivation of PNKP by mutant ATXN3 triggers apoptosis by activating the DNA damage-response pathway in SCA3.PLoS Genet. 2015 Jan 15;11(1):e1004834. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004834. eCollection 2015 Jan. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 25590633 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of the polyglutamine protein ataxin-3 with Rad23 regulates toxicity in Drosophila models of Spinocerebellar Ataxia Type 3.Hum Mol Genet. 2017 Apr 15;26(8):1419-1431. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddx039. Hum Mol Genet. 2017. PMID: 28158474 Free PMC article.
-
FipoQ/FBXO33, a Cullin-1-based ubiquitin ligase complex component modulates ubiquitination and solubility of polyglutamine disease protein.J Neurochem. 2019 Jun;149(6):781-798. doi: 10.1111/jnc.14669. Epub 2019 Feb 28. J Neurochem. 2019. PMID: 30685895
-
Toward therapeutic targets for SCA3: Insight into the role of Machado-Joseph disease protein ataxin-3 in misfolded proteins clearance.Prog Neurobiol. 2015 Sep;132:34-58. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2015.06.004. Epub 2015 Jun 27. Prog Neurobiol. 2015. PMID: 26123252 Review.
-
ATXN3: a multifunctional protein involved in the polyglutamine disease spinocerebellar ataxia type 3.Expert Rev Mol Med. 2024 Sep 25;26:e19. doi: 10.1017/erm.2024.10. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39320846 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The exocyst complex in neurological disorders.Hum Genet. 2023 Aug;142(8):1263-1270. doi: 10.1007/s00439-023-02558-w. Epub 2023 Apr 22. Hum Genet. 2023. PMID: 37085629 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mutant huntingtin induces neuronal apoptosis via derepressing the non-canonical poly(A) polymerase PAPD5.Nat Commun. 2025 Apr 9;16(1):3307. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-58618-4. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40204699 Free PMC article.
-
The protein aggregation inhibitor YAT2150 has potent antimalarial activity in Plasmodium falciparum in vitro cultures.BMC Biol. 2022 Oct 22;20(1):197. doi: 10.1186/s12915-022-01374-4. BMC Biol. 2022. PMID: 36271358 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical analysis to study wild-type and polyglutamine-expanded ATXN3 species.PLoS One. 2024 Dec 23;19(12):e0315868. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0315868. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39715253 Free PMC article.
-
CRL4B E3 ligase recruited by PRPF19 inhibits SARS-CoV-2 infection by targeting ORF6 for ubiquitin-dependent degradation.mBio. 2024 Feb 14;15(2):e0307123. doi: 10.1128/mbio.03071-23. Epub 2024 Jan 24. mBio. 2024. PMID: 38265236 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

