1-O-Hexyl-2,3,5-Trimethylhydroquinone Ameliorates the Development of Preeclampsia through Suppression of Oxidative Stress and Endothelial Cell Apoptosis
- PMID: 33542786
- PMCID: PMC7840260
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/8839394
1-O-Hexyl-2,3,5-Trimethylhydroquinone Ameliorates the Development of Preeclampsia through Suppression of Oxidative Stress and Endothelial Cell Apoptosis
Abstract
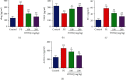
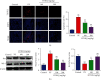
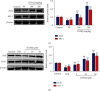
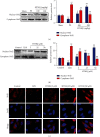
1-O-Hexyl-2,3,5-trimethylhydroquinone (HTHQ), a potent nuclear factor-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) activator, has potent antioxidant activity by scavenging reactive oxygen species (ROS). However, the role of HTHQ on the development of preeclampsia (PE) and the underlying mechanisms have barely been explored. In the present study, PE model was induced by adenovirus-mediated overexpression of soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase 1 (sFlt-1) in pregnant mice. The results showed that HTHQ treatment significantly relieved the high systolic blood pressure (SBP) and proteinuria and increased the fetal weight and fetal weight/placenta weight in preeclamptic mice. Furthermore, we found that HTHQ treatment significantly decreased soluble endoglin (sEng), endothelin-1 (ET-1), and activin A and restored vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in preeclamptic mice. In addition, HTHQ treatment inhibited oxidative stress and endothelial cell apoptosis by increasing the levels of Nrf2 and its downstream haemoxygenase-1 (HO-1) protein. In line with the data in vivo, we discovered that HTHQ treatment attenuated oxidative stress and cell apoptosis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) following hypoxia and reperfusion (H/R), and the HTHQ-mediated protection was lost after transfected with siNrf2. In conclusion, these results suggested that HTHQ ameliorates the development of preeclampsia through suppression of oxidative stress and endothelial cell apoptosis.
Copyright © 2021 Lai Jiang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Neuroprotective effects of 1-O-hexyl-2,3,5-trimethylhydroquinone on ischaemia/reperfusion-induced neuronal injury by activating the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Sep;24(18):10468-10477. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15659. Epub 2020 Jul 17. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32677362 Free PMC article.
-
Negative regulation of soluble Flt-1 and soluble endoglin release by heme oxygenase-1.Circulation. 2007 Apr 3;115(13):1789-97. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.660134. Epub 2007 Mar 26. Circulation. 2007. PMID: 17389265
-
HTHQ (1-O-hexyl-2,3,5-trimethylhydroquinone), an anti-lipid-peroxidative compound: its chemical and biochemical characterizations.Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998 Sep 16;1425(1):47-60. doi: 10.1016/s0304-4165(98)00050-6. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998. PMID: 9813237
-
Evidence-Based Revised View of the Pathophysiology of Preeclampsia.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;956:355-374. doi: 10.1007/5584_2016_168. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 27873232 Review.
-
A possible protective role of Nrf2 in preeclampsia.Ann Anat. 2014 Sep;196(5):268-77. doi: 10.1016/j.aanat.2014.04.002. Epub 2014 May 27. Ann Anat. 2014. PMID: 24954650 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of peroxiredoxin 1 on the regulation of trophoblast function by affecting autophagy and oxidative stress in preeclampsia.J Assist Reprod Genet. 2023 Jul;40(7):1573-1587. doi: 10.1007/s10815-023-02820-0. Epub 2023 May 25. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2023. PMID: 37227568 Free PMC article.
-
Protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor type O (PTPRO) knockdown enhances the proliferative, invasive and angiogenic activities of trophoblast cells by suppressing ER resident protein 44 (ERp44) expression in preeclampsia.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(2):9561-9574. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1997561. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34719307 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of cathepsin C alleviates endothelial cell dysfunction by suppressing p38 MAPK/NF-κB pathway in preeclampsia.Bioengineered. 2022 Feb;13(2):3019-3028. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2023994. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35037834 Free PMC article.
-
Ciprofol attenuates the isoproterenol-induced oxidative damage, inflammatory response and cardiomyocyte apoptosis.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Nov 22;13:1037151. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1037151. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36483733 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of NRF2/KEAP1 Signaling in Preeclampsia.Cells. 2023 Jun 4;12(11):1545. doi: 10.3390/cells12111545. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37296665 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

