Recent Update on the Role of Circular RNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- PMID: 33542907
- PMCID: PMC7851377
- DOI: 10.2147/JHC.S268291
Recent Update on the Role of Circular RNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
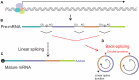
After being overlooked for decades, circular RNAs (circRNAs) have recently generated considerable interest. circRNAs play a role in a variety of normal and pathological biological processes, including hepatocarcinogenesis. Many circRNAs contribute to hepatocarcinogenesis through sponging of microRNAs (miRs) and disruption of cellular signaling pathways that play a part in control of cell proliferation, metastasis and apoptosis. In most cases, overexpressed circRNAs sequester miRs to cause de-repressed translation of mRNAs that encode oncogenic proteins. Conversely, low expression of circRNAs has also been described in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and is associated with inhibited production of tumor suppressor proteins. Other functions of circRNAs that contribute to hepatocarcinogenesis include translation of truncated proteins and acting as adapters to regulate influence of transcription factors on target gene expression. circRNAs also affect hepatocyte transformation indirectly. For example, the molecules regulate immune surveillance of cancerous cells and influence the liver fibrosis that commonly precedes HCC. Marked over- or under-expression of circRNA expression in HCC, with correlating plasma concentrations, has diagnostic utility and assays of these RNAs are being developed as biomarkers of HCC. Although knowledge in the field has recently surged, the myriad of described effects suggests that not all may be vital to hepatocarcinogenesis. Nevertheless, investigation of the role of circRNAs is providing valuable insights that are likely to contribute to improved management of a serious and highly aggressive cancer.
Keywords: HBV; HCC; biomarkers; ceRNA; circRNA; microRNA; signaling pathways.
© 2021 Ely et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

