Overweight and Obesity Among Adult HIV Infected Peoples Receiving ART in Ethiopia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 33543684
- PMCID: PMC7874346
- DOI: 10.1177/2150132721993647
Overweight and Obesity Among Adult HIV Infected Peoples Receiving ART in Ethiopia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: Over-nutrition and diet-linked non-communicable morbidities are showing increasing trend overtime. Even if there are different factors that affect the change in BMI other than ART, several authors have reported increases in BMI among PLHIV on treatment that are equal to or surpass the general population. This study is aimed to estimate the prevalence of obesity and overweight among adult HIV infected peoples taking ART in Ethiopia.
Method: PubMed, CINAHL, Web of science, global health and Google scholar electronic databases were used to perform a systematic literature search. Two authors independently extracted all the necessary data using a structured data extraction format. Data analysis was done using STATA Version 14. The heterogeneity of the studies was assessed by using I2 test. A random-effects model was used to estimate the pooled prevalence. Publication bias was checked using Funnel plot and Egger's test.
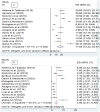
Result: Two thousand seven hundred and fifty-one studies were reviewed and 13 studies fulfilling the inclusion criteria were included in the meta-analysis. The meta-analysis of 13 studies, comprising 4994 participants resulted in pooled prevalence of overweight to be 17.85% (95% CI: 12.22-23.47). Whereas, the pooled prevalence of overweight was found to be 3.90 (95% CI: 2.31-5.49) but after adjusting for publication bias using trim and fill analysis it has become 3.58 (95% CI: 2.04-5.13). Magnitude of both overweight and obesity was higher in studies conducted in Addis Ababa, studies done after 2016 and studies having sample size of less than 400, in subgroup analysis.
Conclusion: The magnitude of overweight and obesity among HIV infected peoples taking ART in Ethiopia is high. There is a need to have a routine screening to PLWHA on the risk of over-nutrition in order to facilitate early detection.
Keywords: ART; Ethiopia; HIV; obesity; overweight.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS [UNAIDS]. Global HIV & AIDS statistics - 2019 fact sheet. 2019. https://www.unaids.org/en/resources/fact-sheet. Accessed November 28, 2020.
-
- Torian L, Chen M, Hall I. HIV surveillance – United States, 1981– 2008. MMWR. 2011;60:689-693. - PubMed
-
- Fanzo J, Hawkes C, Udomkesmalee E, et al. Global Nutrition Report: Shining A Light to Spur Action on Nutrition, 2018.
-
- Doak CM, Wijnhoven TMA, Schokker DF, et al. Age standardization in mapping adult overweight and obesity trends in the who European region. Obes Rev. 2012;13:174-191. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

