Dyshomeostatic modulation of Ca2+-activated K+ channels in a human neuronal model of KCNQ2 encephalopathy
- PMID: 33544076
- PMCID: PMC7864629
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.64434
Dyshomeostatic modulation of Ca2+-activated K+ channels in a human neuronal model of KCNQ2 encephalopathy
Abstract
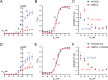
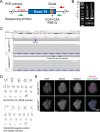
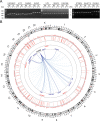
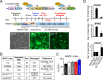
Mutations in KCNQ2, which encodes a pore-forming K+ channel subunit responsible for neuronal M-current, cause neonatal epileptic encephalopathy, a complex disorder presenting with severe early-onset seizures and impaired neurodevelopment. The condition is exceptionally difficult to treat, partially because the effects of KCNQ2 mutations on the development and function of human neurons are unknown. Here, we used induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) and gene editing to establish a disease model and measured the functional properties of differentiated excitatory neurons. We find that patient iPSC-derived neurons exhibit faster action potential repolarization, larger post-burst afterhyperpolarization and a functional enhancement of Ca2+-activated K+ channels. These properties, which can be recapitulated by chronic inhibition of M-current in control neurons, facilitate a burst-suppression firing pattern that is reminiscent of the interictal electroencephalography pattern in patients. Our findings suggest that dyshomeostatic mechanisms compound KCNQ2 loss-of-function leading to alterations in the neurodevelopmental trajectory of patient iPSC-derived neurons.
Keywords: AHP; KCNQ2; M-current; burst-suppression; disease modeling; dyshomeostatic; epileptic encephalopathy; excitatory neurons; homeostatic plasticity; human; human iPSCs; neuroscience; potassium channel; regenerative medicine; stem cells.
© 2021, Simkin et al.
Conflict of interest statement
DS, KM, CV, RD, BB, BP, JO, MF, GR, PP, LL, SL, JM, AG, EK No competing interests declared
Figures

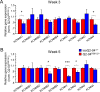
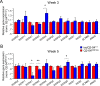
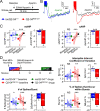
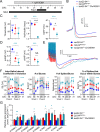
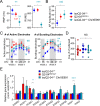
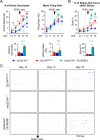
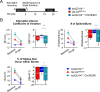
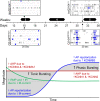

References
-
- Afawi Z, Oliver KL, Kivity S, Mazarib A, Blatt I, Neufeld MY, Helbig KL, Goldberg-Stern H, Misk AJ, Straussberg R, Walid S, Mahajnah M, Lerman-Sagie T, Ben-Zeev B, Kahana E, Masalha R, Kramer U, Ekstein D, Shorer Z, Wallace RH, Mangelsdorf M, MacPherson JN, Carvill GL, Mefford HC, Jackson GD, Scheffer IE, Bahlo M, Gecz J, Heron SE, Corbett M, Mulley JC, Dibbens LM, Korczyn AD, Berkovic SF. Multiplex families with epilepsy: success of clinical and molecular genetic characterization. Neurology. 2016;86:713–722. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000002404. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bardy C, van den Hurk M, Kakaradov B, Erwin JA, Jaeger BN, Hernandez RV, Eames T, Paucar AA, Gorris M, Marchand C, Jappelli R, Barron J, Bryant AK, Kellogg M, Lasken RS, Rutten BP, Steinbusch HW, Yeo GW, Gage FH. Predicting the functional states of human iPSC-derived neurons with single-cell RNA-seq and electrophysiology. Molecular Psychiatry. 2016;21:1573–1588. doi: 10.1038/mp.2016.158. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

