[Treatment options for oligometastatic gastric cancer]
- PMID: 33544151
- PMCID: PMC8159772
- DOI: 10.1007/s00104-021-01353-5
[Treatment options for oligometastatic gastric cancer]
Abstract
Background: At the time of diagnosis of gastric cancer approximately one third of patients already have metastases. It is important to differentiate between oligometastasis and the diffuse metastatic situation. For the first time the definition of oligometastasis has been integrated into the German S3 guidelines.
Objective: Can multimodal treatment with tumor resection and metastasectomy combined with perioperative chemotherapy, increase the chances of survival in oligometastatic patients?
Material and methods: In this review article the data situation of the current literature is discussed.
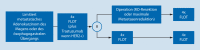
Results: The Dutch D1/D2 trial reported an increased median survival for a subgroup of patients with single metastasis who underwent resection. Multimodal treatment with resection doubled the median survival of oligometastatic patients in the German AIO-FLOT 3 study and as a consequence, the AIO-FLOT 5 (RENAISSANCE) trial was designed. Patients with oligometastatic gastric and esophagogastric junction cancer are randomized after chemotherapy to either undergo resection followed by adjuvant chemotherapy or to undergo definitive chemotherapy. Further randomized trials investigate the benefit of antibodies and immune checkpoint inhibitors in locoregional and advanced metastatic gastric cancer with promising results.
Conclusion: The results of the ongoing randomized trials will show if oligometastatic patients benefit from a multimodal treatment with resection. The clear definition of the oligometastatic state, assessment of the response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy and realistic estimation of the R0 resectability will be useful for patient selection.
Zusammenfassung: HINTERGRUND: Zum Zeitpunkt der Diagnosestellung des Magenkarzinoms haben ca. zwei Drittel der Patienten bereits Metastasen. Wichtig ist es, die Oligometastasierung von der diffus metastasierten Situation abzugrenzen. Die S3-Leitlinie hat die Definition der Oligometastasierung erstmals in die Leitlinie aufgenommen.
Fragestellung: Kann das Überleben von Patienten mit Oligometastasierung mittels Resektion des Tumors und der Metastase kombiniert mit perioperativer Chemotherapie verbessert werden?
Material und methoden: In dieser Übersichtsarbeit wird die Datenlage der aktuellen Literatur dargestellt.
Ergebnisse: Die holländische Magenkarzinomstudie stellte ein verbessertes medianes Überleben für Patienten mit singulären Metastasen fest, wenn diese reseziert wurden. Aufgrund der Resultate der deutschen AIO-FLOT3-Studie, in der sich das mediane Überleben von Patienten mit Oligometastasen mit multimodaler Therapie verdoppelte, wurde die AIO-FLOT5(RENAISSANCE)-Studie initiiert. Diese randomisiert limitiert metastatische Patienten nach neoadjuvanter Chemotherapie entweder zu Resektion gefolgt von Chemotherapie oder zu definitiver Chemotherapie. Weitere randomisierende Studien untersuchen den Nutzen von Antikörpern und Immun-Checkpoint-Inhibitoren beim lokoregionalen und metastasierten Magenkarzinom mit vielversprechenden Resultaten.
Diskussion: Die Resultate der aktuellen Studien werden zeigen, ob Patienten mit Oligometastasierung von einer multimodalen Therapie mit Resektion profitieren. Die eindeutige Definition der Oligometastasierung, eine Beurteilung des Ansprechens nach neoadjuvanter Chemotherapie und eine realistische Einschätzung der R0-Resektion werden bei der entsprechenden Patientenselektion hilfreich sein.
Keywords: Adenocarcinoma of the esophagogastric junction; Diffuse metastasis; Multimodal treatment; Oligometastasis; S3 guidelines.
References
-
- Al-Batran S, Pauligk C, Hofheinz R, et al. Perioperative atezolizumab in combination with FLOT versus FLOT alone in patients with resectable esophagogastric adenocarcinoma: DANTE, a randomized, open-label phase II trial of the German gastric group of the AIO and the SAKK. J Clin Oncol. 2019;37:4142. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2019.37.15_suppl.TPS4142. - DOI
-
- Al-Batran SE, Goetze TO, Mueller DW, et al. The RENAISSANCE (AIO-FLOT5) trial: effect of chemotherapy alone vs. chemotherapy followed by surgical resection on survival and quality of life in patients with limited-metastatic adenocarcinoma of the stomach or esophagogastric junction—a phase III trial of the German AIO/CAO-V/CAOGI. BMC Cancer. 2017;17:893. doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3918-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Al-Batran SE, Hartmann JT, Probst S, et al. Phase III trial in metastatic gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma with fluorouracil, leucovorin plus either oxaliplatin or cisplatin: a study of the Arbeitsgemeinschaft Internistische Onkologie. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:1435–1442. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.13.9378. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Al-Batran SE, Homann N, Pauligk C, et al. Perioperative chemotherapy with fluorouracil plus leucovorin, oxaliplatin, and docetaxel versus fluorouracil or capecitabine plus cisplatin and epirubicin for locally advanced, resectable gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction adenocarcinoma (FLOT4): a randomised, phase 2/3 trial. Lancet. 2019;393:1948–1957. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32557-1. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical