Hypothalamic glucose-sensing mechanisms
- PMID: 33544170
- PMCID: PMC8087998
- DOI: 10.1007/s00125-021-05395-6
Hypothalamic glucose-sensing mechanisms
Abstract
Chronic metabolic diseases, including diabetes and obesity, have become a major global health threat of the twenty-first century. Maintaining glucose homeostasis is essential for survival in mammals. Complex and highly coordinated interactions between glucose-sensing mechanisms and multiple effector systems are essential for controlling glucose levels in the blood. The central nervous system (CNS) plays a crucial role in regulating glucose homeostasis. Growing evidence indicates that disruption of glucose sensing in selective CNS areas, such as the hypothalamus, is closely interlinked with the pathogenesis of obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus. However, the underlying intracellular mechanisms of glucose sensing in the hypothalamus remain elusive. Here, we review the current literature on hypothalamic glucose-sensing mechanisms and discuss the impact of alterations of these mechanisms on the pathogenesis of diabetes.
Keywords: Astrocytes; Brain; Counterregulatory responses; Diabetes; Glucose-sensing; Hypothalamus; Neurons; Obesity; Review; Tanycytes.
Figures
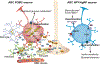

References
-
- Ritter S (2017) Monitoring and maintenance of brain glucose supply importance of hindbrain catecholamine neurons in this multifaceted task. In: Harris RBS (ed) Appetite and food intake: Central control, 2nd edn. CRC Press/Taylor& Francis, Boca Raton, pp 177–204 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

