Early diagnosis of rabies virus infection by RPA-CRISPR techniques in a rat model
- PMID: 33544254
- PMCID: PMC7862975
- DOI: 10.1007/s00705-021-04970-x
Early diagnosis of rabies virus infection by RPA-CRISPR techniques in a rat model
Abstract
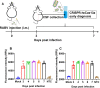
Rabies, which is caused by rabies virus (RABV), poses an ever-present threat to public health in most countries of the world. Once clinical signs appear, the mortality of rabies approaches 100%. To date, no effective method for early rabies diagnosis has been developed. In this study, an RPA-CRISPR nucleic-acid-based assay was developed for early rabies diagnosis by detecting viral RNA shedding in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of rats. This method can detect a single copy of RABV genomic RNA in 1 μL of liquid. RABV genomic RNA released from viral particles in the CSF could be detected via RPA-CRISPR as early as 3 days postinfection in a rat model. This study provides an RPA-CRISPR technique for early detection of RABV with potential application in the clinical diagnosis of human rabies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

