First experience of efficacy and radiation exposure in 320-detector row CT fluoroscopy-guided interventions
- PMID: 33544633
- PMCID: PMC8010553
- DOI: 10.1259/bjr.20200754
First experience of efficacy and radiation exposure in 320-detector row CT fluoroscopy-guided interventions
Abstract
Objective: We investigated the efficacy and exposure to radiation in 320-detector row computed tomography fluoroscopy-guided (CTF-guided) interventions.
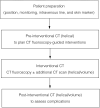
Methods: We analysed 231 320-detector row CTF-guided interventions (207 patients over 2 years and 6 months) in terms of technical success rates, clinical success rates, complications, scanner settings, overall radiation doses (dose-length product, mGy*cm), patient doses of peri-interventional CT series, and interventional CT (including CTF), as a retrospective cohort study. The relationships between patient radiation dose and interventional factors were assessed using multivariate analysis.
Results: Overall technical success rate was 98.7% (228/231). The technical success rates of biopsies, drainages, and aspirations were 98.7% (154/156), 98.5% (66/67), and 100% (8/8), respectively. The clinical success rate of biopsies was 93.5% (146/156). All three major complications occurred in chest biopsies. The median total radiation dose was 522.4 (393.4-819.8) mGy*cm. Of the total radiation dose, 87% was applied during the pre- and post-interventional CT series. Post-interventional CT accounted for 24.4% of the total radiation dose. Only 11.4% of the dose was applied by CTF-guided intervention. Multilinear regression demonstrated that male sex, body mass index, drainage, intervention time, and helical scan as post-interventional CT were significantly associated with higher dose.
Conclusion: The 320-detector row CTF interventions achieved a high success rate. Dose reduction in post-interventional CT provides patient dose reduction without decreasing the technical success rates.
Advances in knowledge: This is the first study on the relationship between various interventional outcomes and patient exposure to radiation in 320-detector row CTF-guided interventions, suggesting a new perspective on dose reduction.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical