New 2-(4-(4-bromophenylsulfonyl)phenyl)-4-arylidene-oxazol-5(4H)-ones: analgesic activity and histopathological assessment
- PMID: 33544801
- PMCID: PMC7864298
- DOI: 10.47162/RJME.61.2.19
New 2-(4-(4-bromophenylsulfonyl)phenyl)-4-arylidene-oxazol-5(4H)-ones: analgesic activity and histopathological assessment
Abstract
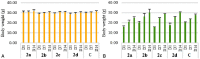
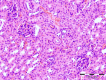
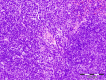
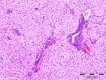
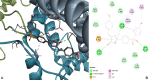
This paper reports the synthesis, analgesic activity, acute toxicity and histopathological (HP) assessment of four new compounds from oxazol-5(4H)-ones class that contain in their molecule a diarylsulfone moiety. The new 2-(4-(4-bromophenylsulfonyl)phenyl)-4-arylidene-oxazol-5(4H)-ones were obtained by reaction of 2-(4-(4-bromophenyl-sulfonyl)benzamido)acetic acid intermediate with aromatic aldehydes (benzaldehyde, 4-methoxy, 4-nitro or 4-bromobenzaldehyde), in acetic anhydride and in the presence of anhydrous sodium acetate. The new compounds have been characterized by spectral techniques, such as: Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), mass spectrometry (MS), proton nuclear magnetic resonance (1H-NMR) and by elemental analysis. The acute toxicity of the new oxazol-5(4H)-ones in mice was assessed through "acute toxic class" method, according to Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) Guidelines. The HP assessment of some preserved organs collected from mice has been performed. The analgesic activity of all new synthesized compounds was carried out with two pharmacological tests: the writhing test and the hot plate test. In order to predict the binding affinities of the synthesized oxazol-5(4H)-ones derivatives against molecular targets involved in pain and inflammation, molecular docking simulations were performed. The results of the writhing test indicated that the most active compound was the oxazolone that contains in the molecule a methoxy group. The acute oral toxicity study revealed no lethal effect of new compounds. The HP assessment of the preserved organs collected from mice did not indicate any cytohistopathological aspects that can be linked to any inflammatory, neoplastic or cytotoxic process, demonstrating the low toxicity of new compounds.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Figures
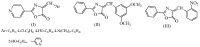
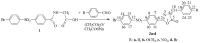



Similar articles
-
New Heterocyclic Compounds from Oxazol-5(4H)-one and 1,2,4-Triazin-6(5H)-one Classes: Synthesis, Characterization and Toxicity Evaluation.Molecules. 2023 Jun 17;28(12):4834. doi: 10.3390/molecules28124834. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37375389 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Synthesis of 4-Benzylidene-2-((1-phenyl-3,4-dihydroisoquinoline-2(1H)-yl)methyl) oxazol-5(4H)-one Derivatives Using 1,2,3,Tetrahydroisoquinoline and their Antimicrobial Activity.Curr Org Synth. 2020;17(5):396-403. doi: 10.2174/1570179417666200415151228. Curr Org Synth. 2020. PMID: 32294044
-
Synthesis, In Silico and In Vitro Evaluation of Antimicrobial and Toxicity Features of New 4-[(4-Chlorophenyl)sulfonyl]benzoic Acid Derivatives.Molecules. 2021 Aug 23;26(16):5107. doi: 10.3390/molecules26165107. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34443693 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and Analgesic Activity of Amines Combining Diazaadamantane and Monoterpene Fragments.Med Chem. 2017;13(8):773-779. doi: 10.2174/1573406413666170525124316. Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28545384
-
Forced degradation and impurity profiling: recent trends in analytical perspectives.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2013 Dec;86:11-35. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2013.07.013. Epub 2013 Jul 31. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2013. PMID: 23969330 Review.
Cited by
-
New Heterocyclic Compounds from Oxazol-5(4H)-one and 1,2,4-Triazin-6(5H)-one Classes: Synthesis, Characterization and Toxicity Evaluation.Molecules. 2023 Jun 17;28(12):4834. doi: 10.3390/molecules28124834. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37375389 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dixit A, Garg G, Sharma NP, Shrivastava DK, Sharma A. Synthesis & biological evaluation of oxazolone derivatives. Curr Res Pharm Sci. 2011;1(2):86–91. http://crpsonline.com/index.php/crps/article/view/42
-
- Parveen M, Ali A, Ahmed S, Malla AM, Alam M, Pereira Silva PS, Ramos Silva M, Lee DU. Synthesis, bioassay, crystal structure and ab initio studies of Erlenmeyer azlactones. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2013;104:538–545. - PubMed
-
- Jat LR, Mishra R, Pathak D. Synthesis and anticancer activity of 4-benzylidene-2-phenyloxazol-5(4H)-one derivatives. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2012;4(1):378–380.
-
- Zhu M, Gokhale VM, Szabo L, Munoz RM, Baek H, Bashyam S, Hurley LH, Von Hoff DD, Han H. Identification of a novel inhibitor of urokinase-type plasminogen activator. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007;6(4):1348–1356. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

