Oral lichen planus - case report
- PMID: 33544810
- PMCID: PMC7864300
- DOI: 10.47162/RJME.61.2.28
Oral lichen planus - case report
Abstract
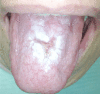
This paper presents the case of a 58-year-old heavy smoker female who came to our clinic with acute pain, as well as mastication and feeding difficulties. The macroscopic examination revealed oral erosive lesions and ulcerations. The polymorphic aspect of the lesions required the differential diagnosis of oral erythroplakia or carcinoma, which were excluded by biopsy. At the same time, we assessed the expression of S100 protein, Ki67 and the cluster of differentiation (CD) 4, CD8 (T-cell) and CD20 (B-cell) immune cell markers by immunohistochemical analysis. As a result, after the clinical and pathological assessment, the diagnosis of oral lichen planus was established, and a therapy plan was conducted. We observed a favorable clinical evolution after the administration of corticosteroids and immunomodulatory agents.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Figures











References
-
- Roopashree MR, Gondhalekar RV, Shashikanth MC, George J, Thippeswamy SH, Shukla A. Pathogenesis of oral lichen planus - a review. J Oral Pathol Med. 2010;39(10):729–734. - PubMed
-
- Vijay P, Pardhe N, Singhal I, Punga R, Singh H. Oral lichen planus: a case report. Int J Oral Health Med Res. 2016;3(3):54–55. http://www.ijohmr.com/upload/Oral%20Lichen%20Planus-%20A%20Case%20Report...
-
- Chiriac A, Foia L, Chiriac AE, Ancuţa C, Manea P, Profire L, Filip F. Lichen planus secondary complications associated with the use of biologic therapy for rheumatoid arthritis. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2013;54(3 Suppl):829–831. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

