Site-specific incorporation of 5'-methyl DNA enhances the therapeutic profile of gapmer ASOs
- PMID: 33544849
- PMCID: PMC7913697
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkab047
Site-specific incorporation of 5'-methyl DNA enhances the therapeutic profile of gapmer ASOs
Abstract
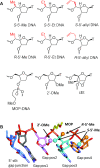
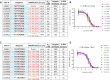
We recently showed that site-specific incorporation of 2'-modifications or neutral linkages in the oligo-deoxynucleotide gap region of toxic phosphorothioate (PS) gapmer ASOs can enhance therapeutic index and safety. In this manuscript, we determined if introducing substitution at the 5'-position of deoxynucleotide monomers in the gap can also enhance therapeutic index. Introducing R- or S-configured 5'-Me DNA at positions 3 and 4 in the oligodeoxynucleotide gap enhanced the therapeutic profile of the modified ASOs suggesting a different positional preference as compared to the 2'-OMe gap modification strategy. The generality of these observations was demonstrated by evaluating R-5'-Me and R-5'-Ethyl DNA modifications in multiple ASOs targeting HDAC2, FXI and Dynamin2 mRNA in the liver. The current work adds to a growing body of evidence that small structural changes can modulate the therapeutic properties of PS ASOs and ushers a new era of chemical optimization with a focus on enhancing the therapeutic profile as opposed to nuclease stability, RNA-affinity and pharmacokinetic properties. The 5'-methyl DNA modified ASOs exhibited excellent safety and antisense activity in mice highlighting the therapeutic potential of this class of nucleic acid analogs for next generation ASO designs.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures




References
-
- Wan W.B., Seth P.P.. The medicinal chemistry of therapeutic oligonucleotides. J. Med. Chem. 2016; 59:9645–9667. - PubMed
-
- Egli M., Manoharan M.. Re-engineering RNA molecules into therapeutic agents. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019; 52:1036–1047. - PubMed
-
- Migawa M.T., Shen W., Wan W.B., Vasquez G., Oestergaard M.E., Low A., De Hoyos C.L., Gupta R., Murray S., Tanowitz M.et al. .. Site-specific replacement of phosphorothioate with alkyl phosphonate linkages enhances the therapeutic profile of gapmer ASOs by modulating interactions with cellular proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019; 47:5465–5479. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

