Human DDK rescues stalled forks and counteracts checkpoint inhibition at unfired origins to complete DNA replication
- PMID: 33545059
- PMCID: PMC8211091
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2021.01.004
Human DDK rescues stalled forks and counteracts checkpoint inhibition at unfired origins to complete DNA replication
Abstract
Eukaryotic genomes replicate via spatially and temporally regulated origin firing. Cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) and Dbf4-dependent kinase (DDK) promote origin firing, whereas the S phase checkpoint limits firing to prevent nucleotide and RPA exhaustion. We used chemical genetics to interrogate human DDK with maximum precision, dissect its relationship with the S phase checkpoint, and identify DDK substrates. We show that DDK inhibition (DDKi) leads to graded suppression of origin firing and fork arrest. S phase checkpoint inhibition rescued origin firing in DDKi cells and DDK-depleted Xenopus egg extracts. DDKi also impairs RPA loading, nascent-strand protection, and fork restart. Via quantitative phosphoproteomics, we identify the BRCA1-associated (BRCA1-A) complex subunit MERIT40 and the cohesin accessory subunit PDS5B as DDK effectors in fork protection and restart. Phosphorylation neutralizes autoinhibition mediated by intrinsically disordered regions in both substrates. Our results reveal mechanisms through which DDK controls the duplication of large vertebrate genomes.
Keywords: ATR; Cdc7; DDK; DNA replication; MERIT40; PDS5B; chemical genetics; phosphoproteomics.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

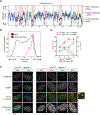

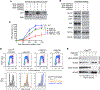



References
-
- Berdougo E, Terret M, and Jallepalli P. (2009). Functional dissection of mitotic regulators through gene targeting in human somatic cells. Methods Mol Biol 545, 21–37. - PubMed
-
- Berti M, Cortez D, and Lopes M. (2020). The plasticity of DNA replication forks in response to clinically relevant genotoxic stress. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

