SARS-CoV-2 diagnosis using medical imaging techniques and artificial intelligence: A review
- PMID: 33545517
- PMCID: PMC7840409
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clinimag.2021.01.019
SARS-CoV-2 diagnosis using medical imaging techniques and artificial intelligence: A review
Abstract
Objective: SARS-CoV-2 is a worldwide health emergency with unrecognized clinical features. This paper aims to review the most recent medical imaging techniques used for the diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 and their potential contributions to attenuate the pandemic. Recent researches, including artificial intelligence tools, will be described.
Methods: We review the main clinical features of SARS-CoV-2 revealed by different medical imaging techniques. First, we present the clinical findings of each technique. Then, we describe several artificial intelligence approaches introduced for the SARS-CoV-2 diagnosis.
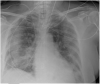
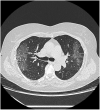
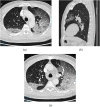
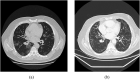
Results: CT is the most accurate diagnostic modality of SARS-CoV-2. Additionally, ground-glass opacities and consolidation are the most common signs of SARS-CoV-2 in CT images. However, other findings such as reticular pattern, and crazy paving could be observed. We also found that pleural effusion and pneumothorax features are less common in SARS-CoV-2. According to the literature, the B lines artifacts and pleural line irregularities are the common signs of SARS-CoV-2 in ultrasound images. We have also stated the different studies, focusing on artificial intelligence tools, to evaluate the SARS-CoV-2 severity. We found that most of the reported works based on deep learning focused on the detection of SARS-CoV-2 from medical images while the challenge for the radiologists is how to differentiate between SARS-CoV-2 and other viral infections with the same clinical features.
Conclusion: The identification of SARS-CoV-2 manifestations on medical images is a key step in radiological workflow for the diagnosis of the virus and could be useful for researchers working on computer-aided diagnosis of pulmonary infections.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Chest CT; Clinical findings; Medical imaging techniques; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
Pneumocystis pneumonia: An important consideration when investigating artificial intelligence-based methods in the radiological diagnosis of COVID-19.Clin Imaging. 2022 May;85:118-119. doi: 10.1016/j.clinimag.2021.02.044. Epub 2021 Mar 26. Clin Imaging. 2022. PMID: 33810937 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Lack of AI-based method for pneumocystis pneumonia classification in radiological diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2.Clin Imaging. 2021 Nov;79:94-95. doi: 10.1016/j.clinimag.2021.03.037. Epub 2021 Apr 21. Clin Imaging. 2021. PMID: 33895561 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak, Geneva: WHO, Available at: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/ novel-coronavirus-2019 2020 (Last accessed 06 November 2020).
-
- World Health Organization. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak, Geneva: WHO, Available at: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus 2019/events-as-they-happen 2020 (Last accessed 13 October 2020).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

