The Role of Hypothalamic Inflammation in Diet-Induced Obesity and Its Association with Cognitive and Mood Disorders
- PMID: 33546219
- PMCID: PMC7913301
- DOI: 10.3390/nu13020498
The Role of Hypothalamic Inflammation in Diet-Induced Obesity and Its Association with Cognitive and Mood Disorders
Abstract
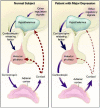
Obesity is often associated with cognitive and mood disorders. Recent evidence suggests that obesity may cause hypothalamic inflammation. Our aim was to investigate the hypothesis that there is a causal link between obesity-induced hypothalamic inflammation and cognitive and mood disorders. Inflammation may influence hypothalamic inter-connections with regions important for cognition and mood, while it may cause dysregulation of the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal (HPA) axis and influence monoaminergic systems. Exercise, healthy diet, and glucagon-like peptide receptor agonists, which can reduce hypothalamic inflammation in obese models, could improve the deleterious effects on cognition and mood.
Keywords: cognitive disorders; dementia; depression; diet; hypothalamic inflammation; mood disorders; obesity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pathways linking obesity to neuropsychiatric disorders.Nutrition. 2019 Oct;66:16-21. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2019.03.017. Epub 2019 Apr 26. Nutrition. 2019. PMID: 31200298 Review.
-
Targeting hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis hormones and sex steroids for improving cognition in major mood disorders and schizophrenia: a systematic review and narrative synthesis.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2018 Jul;93:8-19. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2018.04.012. Epub 2018 Apr 14. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2018. PMID: 29680774
-
Detrimental effects of chronic hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis activation. From obesity to memory deficits.Mol Neurobiol. 1998 Aug;18(1):1-22. doi: 10.1007/BF02741457. Mol Neurobiol. 1998. PMID: 9824846 Review.
-
Ghrelin's Role in the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis Stress Response: Implications for Mood Disorders.Biol Psychiatry. 2015 Jul 1;78(1):19-27. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2014.10.021. Epub 2014 Oct 31. Biol Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 25534754 Review.
-
Future therapeutic targets in mood disorders: the glucocorticoid receptor.Br J Psychiatry. 2000 Nov;177:390-5. doi: 10.1192/bjp.177.5.390. Br J Psychiatry. 2000. PMID: 11059990 Review.
Cited by
-
Enhanced NMDA receptor pathway and glutamate transmission in the hippocampal dentate gyrus mediate the spatial learning and memory impairment of obese rats.Pflugers Arch. 2024 May;476(5):821-831. doi: 10.1007/s00424-024-02924-1. Epub 2024 Feb 28. Pflugers Arch. 2024. PMID: 38416255 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Inflammatory Nutrients and Obesity-Associated Metabolic-Inflammation: State of the Art and Future Direction.Nutrients. 2022 Mar 8;14(6):1137. doi: 10.3390/nu14061137. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35334794 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Links Between Circadian Rhythm Disruption, Melatonin, and Neurodegenerative Diseases: An Updated Review.Molecules. 2025 Apr 23;30(9):1888. doi: 10.3390/molecules30091888. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40363695 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sugar-Sweetened Beverages and Depressive and Social Anxiety Symptoms Among Children and Adolescents Aged 7-17 Years, Stratified by Body Composition.Front Nutr. 2022 May 23;9:888671. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.888671. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35677554 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Aqueous Saffron Extract on Glucoregulation as Well as Hepatic Agt and TNF-α Gene Expression in Rats Subjected to Sub-Chronic Stress.Adv Biomed Res. 2023 May 15;12:117. doi: 10.4103/abr.abr_51_22. eCollection 2023. Adv Biomed Res. 2023. PMID: 37434936 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO|Obesity. [(accessed on 2 May 2020)]; Available online: https://www.who.int/topics/obesity/en/
-
- Kvist H., Sjostrom L., Tylen U. Adipose Tissue Volume Determinations in Women by Computed Tomography: Technical Considerations. Int. J. Obes. 1986;10:53–67. - PubMed
-
- Heilbronn L.K., Rood J., Janderova L., Albu J.B., Kelley D.E., Ravussin E., Smith S.R. Relationship between Serum Resistin Concentrations and Insulin Resistance in Nonobese, Obese, and Obese Diabetic Subjects. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004;89:1844–1848. doi: 10.1210/jc.2003-031410. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

