MicroRNAs: Tiny Regulators of Gene Expression with Pivotal Roles in Normal B-Cell Development and B-Cell Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
- PMID: 33546241
- PMCID: PMC7913321
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13040593
MicroRNAs: Tiny Regulators of Gene Expression with Pivotal Roles in Normal B-Cell Development and B-Cell Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
Abstract
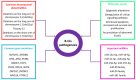
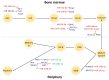
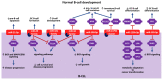
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) represent a class of small non-coding RNAs bearing regulatory potency. The implication of miRNAs in physiological cellular processes has been well documented so far. A typical process orchestrated by miRNAs is the normal B-cell development. A stage-specific expression pattern of miRNAs has been reported in the developmental procedure, as well as interactions with transcription factors that dictate B-cell development. Besides their involvement in normal hematopoiesis, miRNAs are severally implicated in hematological malignancies, a typical paradigm of which is B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL). B-CLL is a highly heterogeneous disease characterized by the accumulation of abnormal B cells in blood, bone marrow, lymph nodes, and spleen. Therefore, timely, specific, and sensitive assessment of the malignancy is vital. Several studies have attempted to highlight the remarkable significance of miRNAs as regulators of gene expression, biomarkers for diagnosis, prognosis, progression, and therapy response prediction, as well as molecules with potential therapeutic utility. This review seeks to outline the linkage between miRNA function in normal and malignant hematopoiesis by demonstrating the main benchmarks of the implication of miRNAs in the regulation of normal B-cell development, and to summarize the key findings about their value as regulators, biomarkers, or therapeutic targets in B-CLL.
Keywords: B-CLL; biomarker; diagnosis; miRNA-transcription factor network; miRNAs; normal B-cell development; prediction; prognosis; progression; regulation; therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Calin G.A., Dumitru C.D., Shimizu M., Bichi R., Zupo S., Noch E., Aldler H., Rattan S., Keating M., Rai K., et al. Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro- RNA genes miR15 and miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2002;99:15524–15529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.242606799. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

