Optimized Detoxification of a Live Attenuated Vaccine Strain (SG9R) to Improve Vaccine Strategy against Fowl Typhoid
- PMID: 33546449
- PMCID: PMC7913755
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines9020122
Optimized Detoxification of a Live Attenuated Vaccine Strain (SG9R) to Improve Vaccine Strategy against Fowl Typhoid
Abstract
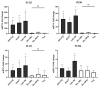
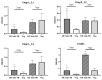
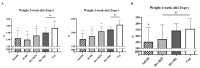
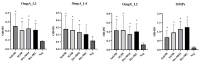
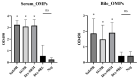
The live attenuated vaccine strain, SG9R, has been used against fowl typhoid worldwide, but it can revert to the pathogenic smooth strain owing to single nucleotide changes such as nonsense mutations in the rfaJ gene. As SG9R possesses an intact Salmonella plasmid with virulence genes, it exhibits dormant pathogenicity and can cause fowl typhoid in young chicks and stressed or immunocompromised brown egg-laying hens. To tackle these issues, we knocked out the rfaJ gene of SG9R (named Safe-9R) to eliminate the reversion risk and generated detoxified strains of Safe-9R by knocking out lpxL, lpxM, pagP, and phoP/phoQ genes to attenuate the virulence. Among the knockout strains, live ΔlpxL- (Dtx-9RL) and ΔlpxM-9R (Dtx-9RM) strains induced remarkably less expression of inflammatory cytokines in chicken macrophage cells, and oil emulsion (OE) Dtx-9RL did not cause body weight loss in chicks. Live Dtx-9RM exhibited efficacy against field strain challenge in one week without any bacterial re-isolation, while the un-detoxified strains showed the development of severe liver lesions and re-isolation of challenged strains. Thus, SG9R was optimally detoxified by knockout of lpxL and lpxM, and Dtx-9RL and Dtx-9RM might be applicable as OE and live vaccines, respectively, to prevent fowl typhoid irrespective of the age of chickens.
Keywords: SG9R; Salmonella enterica serovar Gallinarum biovar Gallinarum; detoxification; lipid A; pro-inflammatory cytokines; vaccines.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
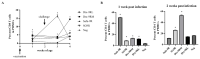
References
-
- Lee Y.-J., Kim K.-S., Kwon Y.-K., Kang M.-S., Mo I.-P., Kim J.-H., Tak R.-B. Prevalent characteristics of fowl typhoid in Korea. J. Vet. Clin. 2003;20:155–158.
-
- De Carli S., Gräf T., Kipper D., Lehmann F.K.M., Zanetti N., Siqueira F.M., Cibulski S., Fonseca A.S.K., Ikuta N., Lunge V.R. Molecular and phylogenetic analyses of Salmonella Gallinarum trace the origin and diversification of recent outbreaks of fowl typhoid in poultry farms. Vet. Microbiol. 2017;212:80–86. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2017.11.001. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Van Immerseel F., Studholme D.J., Eeckhaut V., Heyndrickx M., Dewulf J., Dewaele I., Van Hoorebeke S., Haesebrouck F., Van Meirhaeghe H., Ducatelle R. Salmonella Gallinarum field isolates from laying hens are related to the vaccine strain SG9R. Vaccine. 2013;31:4940–4945. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.08.033. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

