Evaluating a novel, highly sensitive, and quantitative reagent for detecting SARS-CoV-2 antigen
- PMID: 33546959
- PMCID: PMC7836628
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jiac.2021.01.007
Evaluating a novel, highly sensitive, and quantitative reagent for detecting SARS-CoV-2 antigen
Abstract
Introduction: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection is rapidly spreading all over the world. A new quantifying reagent for detecting SARS-CoV-2 antigen was developed for early and accurate detection. We evaluated the novel quantitative reagent for detecting SARS-CoV-2 antigen using an automated laboratory device.
Methods: One-hundred nasopharyngeal samples were collected from 47 SARS-CoV-2-infected patients, and 200 samples were collected from healthy donners. We measured the SARS-CoV-2 antigen and nucleic acid using Lumipulse Presto SARS-CoV-2 Ag and the 2019 Novel Coronavirus Detection Kit, respectively.
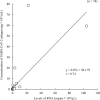
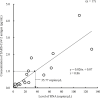
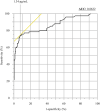
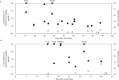
Results: The sensitivity and specificity of the SARS-CoV-2 antigen test were 75.7% (56/74) and 96.0% (192/200), respectively. The concordance rate in the positive group between the antigen and nucleic acid tests was 66% (66/100). In addition, the correlation coefficient between the concentration of SARS-CoV-2 antigen and the level of SARS-CoV-2 RNA was 0.74. There were 19 discrepant samples in which SARS-CoV-2 RNA was detected without SARS-CoV-2 antigen. There was significant difference between the discrepant and matched samples in terms of the time since symptom onset: the 19 discrepant samples were collected a median of 33 days after onset, while the 55 matched samples were collected a median of 19 days after onset. In addition, the 19 discrepant samples were collected from patients who were immune against SARS-CoV-2.
Conclusions: This novel SARS-CoV-2 antigen detection assay is highly sensitive, rapid, accurate, easily diagnostic. It may be useful in both clinical diagnosis and in screening because it does not require special methods such as PCR.
Keywords: Antigen; Detection; Lumipulse; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2021 Japanese Society of Chemotherapy and The Japanese Association for Infectious Diseases. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- World Health Organization Novel coronavirus. nCoV) situation report– 10. 2019. https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/2... Access date: 20 October, 2020.
-
- La Scola B., Le Bideau M., Andreani J., Hoang V.T., Grimaldier C., Colson P., et al. Viral RNA load as determined by cell culture as a management tool for discharge of SARS-CoV-2 patients from infectious disease wards. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2020;39:1059–1061. doi: 10.1007/s10096-020-03913-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

