First-in-Humans Application of 161Tb: A Feasibility Study Using 161Tb-DOTATOC
- PMID: 33547209
- PMCID: PMC8724898
- DOI: 10.2967/jnumed.120.258376
First-in-Humans Application of 161Tb: A Feasibility Study Using 161Tb-DOTATOC
Abstract
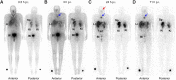
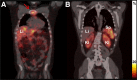
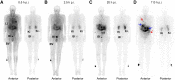
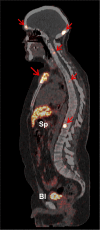
161Tb has decay properties similar to those of 177Lu but, additionally, emits a substantial number of conversion and Auger electrons. The aim of this study was to apply 161Tb in a clinical setting and to investigate the feasibility of visualizing the physiologic and tumor biodistributions of 161Tb-DOTATOC. Methods:161Tb was shipped from Paul Scherrer Institute, Villigen-PSI, Switzerland, to Zentralklinik Bad Berka, Bad Berka, Germany, where it was used for the radiolabeling of DOTATOC. In 2 separate studies, 596 and 1,300 MBq of 161Tb-DOTATOC were administered to a 35-y-old male patient with a metastatic, well-differentiated, nonfunctional malignant paraganglioma and a 70-y-old male patient with a metastatic, functional neuroendocrine neoplasm of the pancreatic tail, respectively. Whole-body planar γ-scintigraphy images were acquired over a period of several days for dosimetry calculations. SPECT/CT images were reconstructed using a recently established protocol and visually analyzed. Patients were observed for adverse events after the application of 161Tb-DOTATOC. Results: The radiolabeling of DOTATOC with 161Tb was readily achieved with a high radiochemical purity suitable for patient application. Planar images and dosimetry provided the expected time-dependent biodistribution of 161Tb-DOTATOC in the liver, kidneys, spleen, and urinary bladder. SPECT/CT images were of high quality and visualized even small metastases in bones and liver. The application of 161Tb-DOTATOC was well tolerated, and no related adverse events were reported. Conclusion: This study demonstrated the feasibility of imaging even small metastases after the injection of relatively low activities of 161Tb-DOTATOC using γ-scintigraphy and SPECT/CT. On the basis of this essential first step in translating 161Tb to clinics, further efforts will be directed toward the application of 161Tb for therapeutic purposes.
Keywords: 161Tb; Auger electrons; DOTATOC; SPECT/CT imaging; first-in-humans.
© 2021 by the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging.
Figures

References
-
- Müller C, Zhernosekov K, Köster U, et al. . A unique matched quadruplet of terbium radioisotopes for PET and SPECT and for α- and β−-radionuclide therapy: an in vivo proof-of-concept study with a new receptor-targeted folate derivative. J Nucl Med. 2012;53:1951–1959. - PubMed
-
- Müller C, Fischer E, Behe M, et al. . Future prospects for SPECT imaging using the radiolanthanide terbium-155: production and preclinical evaluation in tumor-bearing mice. Nucl Med Biol. 2014;41(suppl):e58–e65. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
