Validity and reliability of the EULAR instrument RAID.7 as a tool to assess individual domains of impact of disease in rheumatoid arthritis: a cross-sectional study of 671 patients
- PMID: 33547229
- PMCID: PMC7871340
- DOI: 10.1136/rmdopen-2020-001539
Validity and reliability of the EULAR instrument RAID.7 as a tool to assess individual domains of impact of disease in rheumatoid arthritis: a cross-sectional study of 671 patients
Abstract
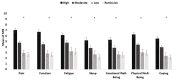
Objective: The rheumatoid arthritis impact of disease (RAID) questionnaire comprises seven patient-important domains of disease impact (pain, function, fatigue, sleep disturbance, emotional well-being, physical well-being, coping). RAID was validated as a pooled-weighted score. Its seven individual items separately could provide a valuable tool in clinical practice to guide interventions targeting the patient's experience of the disease. The aim was to separately assess the psychometric properties of each of the seven numeric rating scale (NRS) of the RAID (RAID.7).
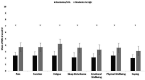
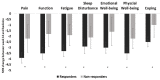
Material and methods: Post hoc analyses of data from the cross-sectional RAID study and from the Rainbow study, an open-label 12-week trial of etanercept in patients with RA. Construct validity of each NRS was assessed cross-sectionally in the RAID data set by Spearman's correlation with the respective external instrument of reference. Using the rainbow data set, we assessed reliability through intraclass correlation coefficient between the screening and the baseline visits and responsiveness (sensitivity to change) by standardised response mean between baseline and 12 weeks.
Results: A total of 671 patients with RA with features of established disease were analysed, 563 and 108 from RAID and Rainbow, respectively. The NRS correlated moderately to strongly with the respective external instrument of reference (r=0.62-0.81). Reliability ranged from 0.64 (0.51-0.74) (pain) to 0.83 (0.76-0.88) (sleep disturbance) and responsiveness from 0.93 (0.73-1.13) (sleep disturbance) to 1.34 (1.01-1.64) (pain).
Conclusion: The separate use of the individual NRS of RAID (RAID.7) is valid, feasible, reliable and sensitive to change, representing an opportunity to improve the assessment and treatment of disease impact with minimal questionnaire burden.
Trial registration number: NCT00768053.
Keywords: arthritis; health care; outcome assessment; patient reported outcome measures; rheumatoid.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2021. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: MD and JAPS have received consultancy fees from Pfizer (advisory board) and their departments have received research grants from Pfizer. TKK has received fees for speaking and/or consulting from Abbvie, Biogen, Celgene, Celltrion, Egis, Evapharma, Ewopharma, Eli Lilly, Gilead, Hikma, Hospira, MSD, Mylan, Novartis, Oktal, Orion Pharma, Pfizer, Roche, Sandoz, Sanofi and UCB and received research funding to Diakonhjemmet Hospital from Abbvie, BMS, MSD, Pfizer, Roche and UCB.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Finalisation and validation of the rheumatoid arthritis impact of disease score, a patient-derived composite measure of impact of rheumatoid arthritis: a EULAR initiative.Ann Rheum Dis. 2011 Jun;70(6):935-42. doi: 10.1136/ard.2010.142901. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011. PMID: 21540201
-
The revised Bristol Rheumatoid Arthritis Fatigue measures and the Rheumatoid Arthritis Impact of Disease scale: validation in six countries.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2018 Feb 1;57(2):300-308. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kex370. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2018. PMID: 29087507 Free PMC article.
-
Psychometric properties of sleep and coping numeric rating scales in rheumatoid arthritis: a subanalysis of an etanercept trial.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2017 Sep-Oct;35(5):786-790. Epub 2017 Mar 23. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2017. PMID: 28339355 Clinical Trial.
-
Patient-reported outcomes in Asia: evaluation of the properties of the Rheumatoid Arthritis Impact of Disease (RAID) score in multiethnic Asian patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Clin Rheumatol. 2017 May;36(5):1149-1154. doi: 10.1007/s10067-016-3522-4. Epub 2016 Dec 30. Clin Rheumatol. 2017. PMID: 28039541
-
European multicentre pilot survey to assess vitamin D status in rheumatoid arthritis patients and early development of a new Patient Reported Outcome questionnaire (D-PRO).Autoimmun Rev. 2017 May;16(5):548-554. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2017.03.002. Epub 2017 Mar 6. Autoimmun Rev. 2017. PMID: 28279841 Review.
Cited by
-
Development of the Rheumatoid Arthritis Distress Scale (RADS): a new tool to identify disease-specific distress in patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis.BMC Rheumatol. 2021 Nov 16;5(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s41927-021-00220-4. BMC Rheumatol. 2021. PMID: 34782021 Free PMC article.
-
Residual pain and fatigue are affected by disease perception in rheumatoid arthritis in sustained clinical and ultrasound remission.Clin Rheumatol. 2025 Mar;44(3):1019-1029. doi: 10.1007/s10067-025-07331-0. Epub 2025 Jan 22. Clin Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 39841373 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical performance of rheumatoid arthritis impact of disease score: a real-life evidence from the multicenter nationwide registry BioStaR.Rheumatol Int. 2021 Nov;41(11):1971-1978. doi: 10.1007/s00296-021-04992-3. Epub 2021 Sep 24. Rheumatol Int. 2021. PMID: 34559275
-
Protocol for a pragmatic feasibility randomised controlled trial of peer coaching for adults with long-term conditions: PEER CONNECT.BMJ Open. 2022 Sep 29;12(9):e059966. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-059966. BMJ Open. 2022. PMID: 36175099 Free PMC article.
-
Is the Rheumatoid Arthritis Impact of Disease (RAID) score a meaningful instrument for other inflammatory rheumatic diseases? A cross-sectional analysis of data from the German National Database.RMD Open. 2022 Jul;8(2):e002342. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2022-002342. RMD Open. 2022. PMID: 35793877 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
