Rapid electrochemical detection of coronavirus SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 33547323
- PMCID: PMC7864991
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-21121-7
Rapid electrochemical detection of coronavirus SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a highly contagious disease caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Diagnosis of COVID-19 depends on quantitative reverse transcription PCR (qRT-PCR), which is time-consuming and requires expensive instrumentation. Here, we report an ultrasensitive electrochemical biosensor based on isothermal rolling circle amplification (RCA) for rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2. The assay involves the hybridization of the RCA amplicons with probes that were functionalized with redox active labels that are detectable by an electrochemical biosensor. The one-step sandwich hybridization assay could detect as low as 1 copy/μL of N and S genes, in less than 2 h. Sensor evaluation with 106 clinical samples, including 41 SARS-CoV-2 positive and 9 samples positive for other respiratory viruses, gave a 100% concordance result with qRT-PCR, with complete correlation between the biosensor current signals and quantitation cycle (Cq) values. In summary, this biosensor could be used as an on-site, real-time diagnostic test for COVID-19.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

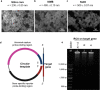
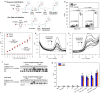
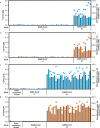
References
-
- WHO. Clinical care of severe acute respiratory infections—Tool kit. Available from https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/clinical-care-of-severe-acute-re... (2020).
-
- WHO. Transmission of SARS-CoV-2: implications for infection prevention precautions. Available from https://www.who.int/news-room/commentaries/detail/transmission-of-sars-c... (2020).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

