Clinical epigenomics: genome-wide DNA methylation analysis for the diagnosis of Mendelian disorders
- PMID: 33547396
- PMCID: PMC8187150
- DOI: 10.1038/s41436-020-01096-4
Clinical epigenomics: genome-wide DNA methylation analysis for the diagnosis of Mendelian disorders
Erratum in
-
Correction: Clinical epigenomics: genome-wide DNA methylation analysis for the diagnosis of Mendelian disorders.Genet Med. 2021 Nov;23(11):2228. doi: 10.1038/s41436-021-01130-z. Genet Med. 2021. PMID: 33637969 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Purpose: We describe the clinical implementation of genome-wide DNA methylation analysis in rare disorders across the EpiSign diagnostic laboratory network and the assessment of results and clinical impact in the first subjects tested.
Methods: We outline the logistics and data flow between an integrated network of clinical diagnostics laboratories in Europe, the United States, and Canada. We describe the clinical validation of EpiSign using 211 specimens and assess the test performance and diagnostic yield in the first 207 subjects tested involving two patient subgroups: the targeted cohort (subjects with previous ambiguous/inconclusive genetic findings including genetic variants of unknown clinical significance) and the screening cohort (subjects with clinical findings consistent with hereditary neurodevelopmental syndromes and no previous conclusive genetic findings).
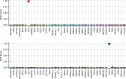
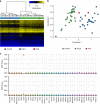
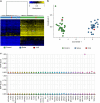
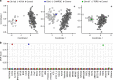
Results: Among the 207 subjects tested, 57 (27.6%) were positive for a diagnostic episignature including 48/136 (35.3%) in the targeted cohort and 8/71 (11.3%) in the screening cohort, with 4/207 (1.9%) remaining inconclusive after EpiSign analysis.
Conclusion: This study describes the implementation of diagnostic clinical genomic DNA methylation testing in patients with rare disorders. It provides strong evidence of clinical utility of EpiSign analysis, including the ability to provide conclusive findings in the majority of subjects tested.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Christianson, A., Howson, C. & Modell, B. Global report on birth defect. The hidden toll of dying and disabled children. (New York, March of Dimes, 2006).
-
- Kvarnung, M. & Nordgren, A. Intellectual disability & rare disorders: a diagnostic challenge. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol.10.1007/978-3-319-67144-4_3 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Schwarze, K., Buchanan, J., Taylor, J. C. & Wordsworth, S. Are whole-exome and whole-genome sequencing approaches cost-effective? A systematic review of the literature. Genet. Med. 20, 1122–1130 (2018). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

