Soil depth matters: shift in composition and inter-kingdom co-occurrence patterns of microorganisms in forest soils
- PMID: 33547899
- PMCID: PMC7948073
- DOI: 10.1093/femsec/fiab022
Soil depth matters: shift in composition and inter-kingdom co-occurrence patterns of microorganisms in forest soils
Abstract
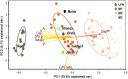
Soil depth represents a strong physiochemical gradient that greatly affects soil-dwelling microorganisms. Fungal communities are typically structured by soil depth, but how other microorganisms are structured is less known. Here, we tested whether depth-dependent variation in soil chemistry affects the distribution and co-occurrence patterns of soil microbial communities. This was investigated by DNA metabarcoding in conjunction with network analyses of bacteria, fungi, as well as other micro-eukaryotes, sampled in four different soil depths in Norwegian birch forests. Strong compositional turnover in microbial assemblages with soil depth was detected for all organismal groups. Significantly greater microbial diversity and fungal biomass appeared in the nutrient-rich organic layer, with sharp decrease towards the less nutrient-rich mineral zones. The proportions of copiotrophic bacteria, Arthropoda and Apicomplexa were markedly higher in the organic layer, while patterns were opposite for oligotrophic bacteria, Cercozoa, Ascomycota and ectomycorrhizal fungi. Network analyses indicated more intensive inter-kingdom co-occurrence patterns in the upper mineral layer (0-5 cm) compared to the above organic and the lower mineral soil, signifying substantial influence of soil depth on biotic interactions. This study supports the view that different microbial groups are adapted to different forest soil strata, with varying level of interactions along the depth gradient.
Keywords: Betula pubescens; boreal birch forest; co-occurrences patterns; metabarcoding; microbial communities; microbial interactions.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of FEMS.
Figures





References
-
- Anderson IC, Campbell CD, Prosser JI.. Potential bias of fungal 18S rDNA and internal transcribed spacer polymerase chain reaction primers for estimating fungal biodiversity in soil. Environ Microbiol. 2003;5:36–47. - PubMed
-
- Anderson IC, Genney DR, Alexander IJ.. Fine-scale diversity and distribution of ectomycorrhizal fungal mycelium in a Scots pine forest. New Phytol. 2014;201:1423–30. - PubMed
-
- Asplund J, Kauserud H, Ohlson Met al. Spruce and beech as local determinants of forest fungal community structure in litter, humus and mineral soil. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2018;95:fiy232. - PubMed
-
- Bahram M, Hildebrand F, Forslund SKet al. Structure and function of the global topsoil microbiome. Nature. 2018;560:233–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

