Highly multiplexed tissue imaging using repeated oligonucleotide exchange reaction
- PMID: 33548142
- PMCID: PMC8251877
- DOI: 10.1002/eji.202048891
Highly multiplexed tissue imaging using repeated oligonucleotide exchange reaction
Abstract
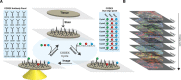
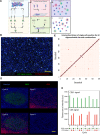
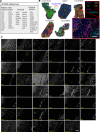
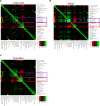
Multiparameter tissue imaging enables analysis of cell-cell interactions in situ, the cellular basis for tissue structure, and novel cell types that are spatially restricted, giving clues to biological mechanisms behind tissue homeostasis and disease. Here, we streamlined and simplified the multiplexed imaging method CO-Detection by indEXing (CODEX) by validating 58 unique oligonucleotide barcodes that can be conjugated to antibodies. We showed that barcoded antibodies retained their specificity for staining cognate targets in human tissue. Antibodies were visualized one at a time by adding a fluorescently labeled oligonucleotide complementary to oligonucleotide barcode, imaging, stripping, and repeating this cycle. With this we developed a panel of 46 antibodies that was used to stain five human lymphoid tissues: three tonsils, a spleen, and a LN. To analyze the data produced, an image processing and analysis pipeline was developed that enabled single-cell analysis on the data, including unsupervised clustering, that revealed 31 cell types across all tissues. We compared cell-type compositions within and directly surrounding follicles from the different lymphoid organs and evaluated cell-cell density correlations. This sequential oligonucleotide exchange technique enables a facile imaging of tissues that leverages pre-existing imaging infrastructure to decrease the barriers to broad use of multiplexed imaging.
Keywords: CODEX; DNA-conjugated antibodies; Multiplexed tissue imaging; Single-cell analysis; Spatial single-cell biology.
© 2021 The Authors. European Journal of Immunology published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
J.K.D. is an employee of Akoya Biosciences, Inc. G.P.N. received research grants from Pfizer, Inc., Vaxart, Inc., Celgene, Inc., and Juno Therapeutics, Inc. during the course of this work. N.S., Y.G., and G.P.N. are inventors on US patent 9909167, granted to Stanford University that covers some aspects of the technology described in this article. J.K.D., N.S., Y.G., and G.P.N. have equity in and/or are scientific advisory board members of Akoya Biosciences, Inc. C.M.S. is a scientific advisor to Enable Medicine, LLC. The other authors declare no commercial or financial conflict of interests.
Figures


References
-
- Thommen, D. S. , Koelzer, V. H. , Herzig, P. , Roller, A. , Trefny, M. , Dimeloe, S. , Kiialainen, A. et al., A transcriptionally and functionally distinct PD‐1+ CD8+ T cell pool with predictive potential in non‐small‐cell lung cancer treated with PD‐1 blockade. Nat. Med. 2018. 24: 994–1004. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dieu‐Nosjean, M. ‐C. , Goc, J. , Giraldo, N. A. , Sautès‐Fridman, C. and Fridman, W. H. , Tertiary lymphoid structures in cancer and beyond. Trends Immunol. 2014. 35: 571–580. - PubMed
-
- Sautès‐Fridman, C. , Petitprez, F. , Calderaro, J. and Fridman, W. H. , Tertiary lymphoid structures in the era of cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2019. 19: 307–325. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- 27145/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- UG3 DK114937/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI100627/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL120724/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG010426/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- F99 CA212231/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI140498/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA196585/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R33 CA183692/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI135976/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI131374/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI057229/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U2C CA233238/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- C27165/A29073/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- U01 AI101984/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- F32 CA233203/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL108797/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U2C CA233195/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL128173/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

