How glycobiology can help us treat and beat the COVID-19 pandemic
- PMID: 33548227
- PMCID: PMC7857991
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100375
How glycobiology can help us treat and beat the COVID-19 pandemic
Abstract
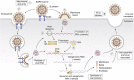
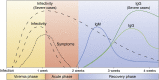
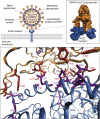
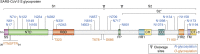
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) emerged during the last months of 2019, spreading throughout the world as a highly transmissible infectious illness designated as COVID-19. Vaccines have now appeared, but the challenges in producing sufficient material and distributing them around the world means that effective treatments to limit infection and improve recovery are still urgently needed. This review focuses on the relevance of different glycobiological molecules that could potentially serve as or inspire therapeutic tools during SARS-CoV-2 infection. As such, we highlight the glycobiology of the SARS-CoV-2 infection process, where glycans on viral proteins and on host glycosaminoglycans have critical roles in efficient infection. We also take notice of the glycan-binding proteins involved in the infective capacity of virus and in human defense. In addition, we critically evaluate the glycobiological contribution of candidate drugs for COVID-19 therapy such as glycans for vaccines, anti-glycan antibodies, recombinant lectins, lectin inhibitors, glycosidase inhibitors, polysaccharides, and numerous glycosides, emphasizing some opportunities to repurpose FDA-approved drugs. For the next-generation drugs suggested here, biotechnological engineering of new probes to block the SARS-CoV-2 infection might be based on the essential glycobiological insight on glycosyltransferases, glycans, glycan-binding proteins, and glycosidases related to this pathology.
Keywords: COVID-19; FDA-approved drugs; SARS-CoV-2; glycobiology; potential therapies.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures
References
-
- He X., Lau E.H.Y., Wu P., Deng X., Wang J., Hao X., Lau Y.C., Wong J.Y., Guan Y., Tan X., Mo X., Chen Y., Liao B., Chen W., Hu F. Temporal dynamics in viral shedding and transmissibility of COVID-19. Nat. Med. 2020;26:672–675. - PubMed
-
- Zhang J., Litvinova M., Wang W., Wang Y., Deng X., Chen X.X., Li M., Zheng W., Yi L., Chen X.X., Wu Q., Liang Y., Wang X., Yang J., Sun K. Evolving epidemiology and transmission dynamics of coronavirus disease 2019 outside Hubei province, China: a descriptive and modelling study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020;20:793–802. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

