Simultaneous quantification of seven repurposed COVID-19 drugs remdesivir (plus metabolite GS-441524), chloroquine, hydroxychloroquine, lopinavir, ritonavir, favipiravir and azithromycin by a two-dimensional isotope dilution LC-MS/MS method in human serum
- PMID: 33548872
- PMCID: PMC7843035
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpba.2021.113935
Simultaneous quantification of seven repurposed COVID-19 drugs remdesivir (plus metabolite GS-441524), chloroquine, hydroxychloroquine, lopinavir, ritonavir, favipiravir and azithromycin by a two-dimensional isotope dilution LC-MS/MS method in human serum
Abstract
Background: The present COVID-19 pandemic has prompted worldwide repurposing of drugs. The aim of the present work was to develop and validate a two-dimensional isotope-dilution liquid chromatrography tandem mass spectrometry (ID-LC-MS/MS) method for accurate quantification of remdesivir and its active metabolite GS-441524, chloroquine, hydroxychloroquine, lopinavir, ritonavir, favipiravir and azithromycin in serum; drugs that have gained attention for repurposing in the treatment of COVID-19.
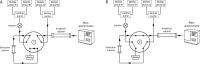
Methods: Following protein precipitation, samples were separated with a two-dimensional ultra-high performance liquid chromatography (2D-UHPLC) setup, consisting of an online solid phase extraction (SPE) coupled to an analytical column. For quantification, stable isotope-labelled analogues were used as internal standards for all analytes. The method was validated on the basis of the European Medicines Agency bioanalytical method validation protocol.
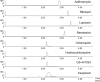
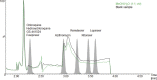
Results: Detuning of lopinavir and ritonavir allowed simultaneous quantification of all analytes with different concentration ranges and sensitivity with a uniform injection volume of 5 μL. The method provided robust validation results with inaccuracy and imprecision values of ≤ 9.59 % and ≤ 11.1 % for all quality controls.
Conclusion: The presented method is suitable for accurate and simultaneous quantification of remdesivir, its metabolite GS-441525, chloroquine, hydroxychloroquine, lopinavir, ritonavir, favipiravir and azithromycin in human serum. The quantitative assay may be an efficient tool for the therapeutic drug monitoring of these potential drug candidates in COVID-19 patients in order to increase treatment efficacy and safety.
Keywords: Antiviral therapy; Isotope dilution liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (ID-LC–MS/MS); Therapeutic drug monitoring.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

