Ursolic acid induces apoptosis and anoikis in colorectal carcinoma RKO cells
- PMID: 33549076
- PMCID: PMC7866452
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-021-03232-2
Ursolic acid induces apoptosis and anoikis in colorectal carcinoma RKO cells
Abstract
Background: Ursolic acid (UA) is an anti-cancer herbal compound. In the present study, we observed the effects of UA on anchorage-dependent and -independent growth of human colorectal cancer (CRC) RKO cells.
Methods: RKO cells were cultured in conventional and detached condition and treated with UA. Cell viability was evaluated by CCK-8 assay. Cell cycle was analyzed by flow cytometry. Apoptosis was identified by Hoechst 33258 staining and flow cytometry analysis. Activities of caspases were measured by commercial kits. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) was recognized by DCFH-DA fluorescent staining. Anoikis was identified by EthD-1 fluorescent staining and flow cytometry analysis. Expression and phosphorylation of proteins were analyzed by western blot.
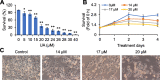
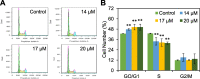
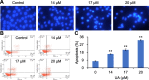
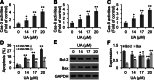
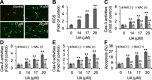
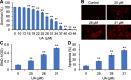
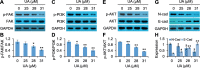
Results: UA inhibited RKO cell viability in both a dose- and time-dependent manner. UA arrested the cell cycle at the G0/G1 phase, and induced caspase-dependent apoptosis. UA inhibited Bcl-2 expression and increased Bax expression. In addition, UA up-regulated the level of ROS that contributed to UA activated caspase-3, - 8 and - 9, and induced apoptosis. Furthermore, UA inhibited cell growth in a detached condition and induced anoikis in RKO cells that was accompanied by dampened phosphorylation of FAK, PI3K and AKT. UA also inhibited epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) as indicated by the down-regulation of N-Cad expression and up-regulation of E-Cad expression.
Conclusions: UA induced caspase-dependent apoptosis, and FAK/PI3K/AKT singling and EMT related anoikis in RKO cells. UA was an effective anti-cancer compound against both anchorage-dependent and -independent growth of RKO cells.
Keywords: AKT; Anoikis; Apoptosis; Caspases; Colorectal cancer; Epithelial-mesenchymal transition; FAK; PI3K; Reactive oxygen species; Ursolic acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Hu B, Shen KP, Shi XF, Deng S, Wei MM. Root of Actinidia chinensis planch induces anoikis in colon carcinoma RKO cells. Chin J Exp Trad med form. 2013;19(16):242–245.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

