Advance of structural modification of nucleosides scaffold
- PMID: 33550179
- PMCID: PMC7995807
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2021.113233
Advance of structural modification of nucleosides scaffold
Abstract
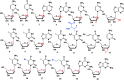
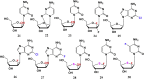
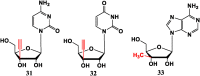
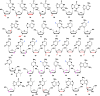
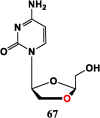
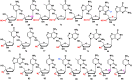
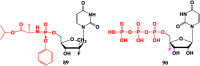
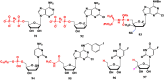
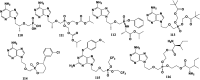
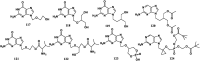
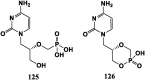
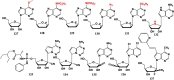
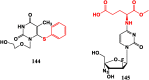
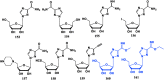
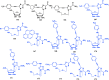
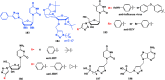
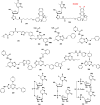
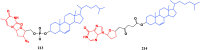
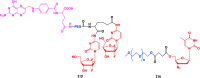
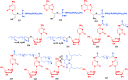
With Remdesivir being approved by FDA as a drug for the treatment of Corona Virus Disease 2019 (COVID-19), nucleoside drugs have once again received widespread attention in the medical community. Herein, we summarized modification of traditional nucleoside framework (sugar + base), traizole nucleosides, nucleoside analogues assembled by other drugs, macromolecule-modified nucleosides, and their bioactivity rules. 2'-"Ara"-substituted by -F or -CN group, and 3'-"ara" substituted by acetylenyl group can greatly influence their anti-tumor activities. Dideoxy dehydrogenation of 2',3'-sites can enhance antiviral efficiencies. Acyclic nucleosides and L-type nucleosides mainly represented antiviral capabilities. 5-F Substituted uracil analogues exihibit anti-tumor effects, and the substrates substituted by -I, -CF3, bromovinyl group usually show antiviral activities. The sugar coupled with 1-N of triazolid usually displays anti-tumor efficiencies, while the sugar coupled with 2-N of triazolid mainly represents antiviral activities. The nucleoside analogues assembled by cholesterol, polyethylene glycol, fatty acid and phospholipid would improve their bioavailabilities and bioactivities, or reduce their toxicities.
Keywords: Anti-tumor; Antiviral; Nucleosides scaffold; Prodrugs; Triazoles.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

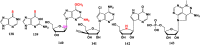
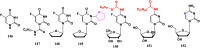


References
-
- Jazayeri A., Falck J., Lukas C., Bartek J., Smith G.C.M., Lukas J., Jackson S.P. ATM-and cell cycle-dependent regulation of ATR in response to DNA double-strand breaks. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006;8:37–45. - PubMed
-
- Ewald B., Sampath D., Plunkett W. Nucleoside analogs: molecular mechanisms signaling cell death. Oncogene. 2008;27:6522–6537. - PubMed
-
- Sheahan T.P., Sims A.C., Leist S.R., Schäfer A., Won J., Brown A.J., Montgomery S.A., Hogg A., Babusis D., Clarke M.O., Spahn J.E., Bauer L., Sellers S., Porter D., Feng J.Y., Cihlar T., Jordan R., Denison M.R., Baric R.S. Comparative therapeutic efficacy of Remdesivir and combination Lopinavir, Ritonavir, and interferon beta against MERS-CoV. Nat. Commun. 2020;11:e222. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

