New closed-loop insulin systems
- PMID: 33550442
- PMCID: PMC8012332
- DOI: 10.1007/s00125-021-05391-w
New closed-loop insulin systems
Erratum in
-
Correction to: New closed-loop insulin systems.Diabetologia. 2021 Jun;64(6):1455. doi: 10.1007/s00125-021-05443-1. Diabetologia. 2021. PMID: 33751132 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
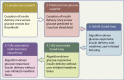
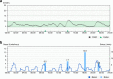
Advances in diabetes technologies have enabled the development of automated closed-loop insulin delivery systems. Several hybrid closed-loop systems have been commercialised, reflecting rapid transition of this evolving technology from research into clinical practice, where it is gradually transforming the management of type 1 diabetes in children and adults. In this review we consider the supporting evidence in terms of glucose control and quality of life for presently available closed-loop systems and those in development, including dual-hormone closed-loop systems. We also comment on alternative 'do-it-yourself' closed-loop systems. We remark on issues associated with clinical adoption of these approaches, including training provision, and consider limitations of presently available closed-loop systems and areas for future enhancements to further improve outcomes and reduce the burden of diabetes management.
Keywords: Artificial pancreas; Automated insulin delivery; Hybrid closed-loop; Review; Type 1 diabetes.
Figures


References
-
- El Youssef J, Castle J, Ward WK (2009) A review of closed-loop algorithms for glycemic control in the treatment of type 1 diabetes. Algorithms 2(1):518–532. 10.3390/a2010518
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

