Quality of life in patients with type 2 diabetes after switching to insulin degludec: results from a cross-sectional survey
- PMID: 33550540
- PMCID: PMC8178133
- DOI: 10.1007/s11136-020-02753-6
Quality of life in patients with type 2 diabetes after switching to insulin degludec: results from a cross-sectional survey
Abstract
Purpose: Five quality of life (QoL) domains are particularly important to patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) using basal insulin-sense of physical well-being, sense of safety regarding hypoglycemia, sense of diabetes as burdensome, feelings of freedom and flexibility, and sleep quality.
Methods: An online survey assessed these QoL domains in adult patients with T2D in the USA who had switched from a previous basal insulin to insulin degludec (IDeg): modified versions of the World Health Organization (Five) Well-Being Index (WHO-5), Hypoglycemia Attitudes and Behavior Scale (HABS; confidence and anxiety subscales only), and Diabetes Distress Scale (DDS; emotional burden and regimen-related distress subscales only); three items assessing feelings of freedom and flexibility; and one item assessing sleep quality (hours of restful sleep). Patients rated each item for their previous basal insulin and currently while using IDeg. Correlations between sleep quality and the other QoL scales were also assessed.
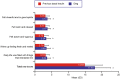
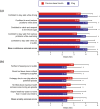
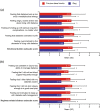
Results: In total, 152 patients completed the survey and were included in the study sample. Patients reported significantly improved scores while using IDeg on all WHO-5, DDS, HABS, feelings of freedom and flexibility item scores, and total raw/mean subscale scores (P < 0.0001). Patients also reported a significantly greater number of hours of restful sleep [mean (SD) 6.6 (2.0) vs. 5.5 (1.8); P < 0.0001]. Better sleep quality statistically significantly correlated with improved QoL in all other domains assessed.
Conclusions: Treatment with IDeg after switching from a previous basal insulin was associated with statistically significant improvements in all QoL domains assessed.
Keywords: Basal insulin; Hypoglycemia; Insulin degludec; Insulin glargine; Quality of life; Type 2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
When insulin degludec enhances quality of life in patients with type 2 diabetes: a qualitative investigation.Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2018 May 3;16(1):87. doi: 10.1186/s12955-018-0883-1. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2018. PMID: 29720273 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin degludec early clinical experience: does the promise from the clinical trials translate into clinical practice--a case-based evaluation.J Med Econ. 2015 Feb;18(2):96-105. doi: 10.3111/13696998.2014.975234. Epub 2014 Oct 29. J Med Econ. 2015. PMID: 25325179
-
Effect of insulin degludec versus insulin glargine on glycemic control and daily fasting blood glucose variability in insulin-naïve Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes: I'D GOT trial.Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2017 Aug;130:237-243. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2017.06.007. Epub 2017 Jun 15. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2017. PMID: 28651211 Clinical Trial.
-
A Review of the Clinical Efficacy and Safety of Insulin Degludec and Glargine 300 U/mL in the Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus.Clin Ther. 2017 Aug;39(8S2):S12-S33. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2017.01.007. Epub 2017 Feb 7. Clin Ther. 2017. PMID: 28187863 Review.
-
Insulin degludec results in lower rates of nocturnal hypoglycaemia and fasting plasma glucose vs. insulin glargine: A meta-analysis of seven clinical trials.Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2015 Oct;25(10):898-905. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2015.06.005. Epub 2015 Jun 18. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2015. PMID: 26232910 Review.
Cited by
-
How Might We Tell if Advances in Diabetes Care and Technology are Helping People to Feel Less Constrained? Introducing the Diabetes Constraints Scale.J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2024 Dec 26:19322968241308269. doi: 10.1177/19322968241308269. Online ahead of print. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2024. PMID: 39726263 Free PMC article.
-
Concept analysis of diabetes-related quality of life.Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2025 Mar 24;23(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s12955-025-02354-2. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2025. PMID: 40128774 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Garber AJ, Abrahamson MJ, Barzilay JI, Blonde L, Bloomgarden ZT, Bush MA, et al. Consensus statement by the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology on the comprehensive type 2 diabetes management algorithm: 2020 executive summary. Endocrine Practice. 2020;26:107–139. doi: 10.4158/CS-2019-0472. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Novo Nordisk Inc . Tresiba® (insulin degludec injection) 100 U/mL, 200 U/mL. US prescribing information. Plainsboro, NJ: Novo Nordisk Inc; 2019.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

