Rupture of De Novo Middle Cerebral Artery Aneurysm 8 Years After the Clipping of Ruptured M1 Middle Cerebral Artery Aneurysm
- PMID: 33551447
- PMCID: PMC7883815
- DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.929194
Rupture of De Novo Middle Cerebral Artery Aneurysm 8 Years After the Clipping of Ruptured M1 Middle Cerebral Artery Aneurysm
Abstract
BACKGROUND Development and rupture of a de novo intracranial aneurysm is rare. Little is known regarding its etiology and the appropriate timing of follow-up angiograms after surgical clipping or coiling. CASE REPORT We present a case report of a 39-year-old male smoker with history of hypertension who developed a de novo aneurysm 8 years after surgical clipping of an aneurysm in the middle cerebral artery in the same segment. He presented with neck rigidity and drowsiness. Laboratory analysis did not show blood dyscrasia. Brain computerized tomography showed right temporal lobe hematoma and 4-vessel angiogram demonstrated de novo aneurysm in the same segment of the M1 middle cerebral artery, which was confirmed by intraoperative microsurgical findings. We review the literature on such cases and discuss the pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment of this condition. De novo aneurysm, although rare, can develop within days to as long as 10 years after surgical clipping or coiling. CONCLUSIONS This rare case of de novo aneurysm supports follow-up imaging of patients after initial surgical clipping for up to 10 years.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
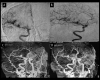
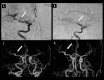
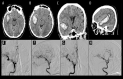

References
-
- Juvela S, Poussa K, Porras M. Factors affecting formation and growth of intracranial aneurysms: A long-term follow-up study. Stroke. 2001;32:485–91. - PubMed
-
- Burkhardt JK, Chua MHJ, Weiss M, et al. Risk of aneurysm residual regrowth, recurrence, and de novo aneurysm formation after microsurgical clip occlusion based on follow-up with catheter angiography. World Neurosurg. 2017;106:74–84. - PubMed
-
- Giordano E, Lanzino G, Rangel-Castillo L, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis. J Neurosurg. 2019;131:14–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

