Materials for blood brain barrier modeling in vitro
- PMID: 33551572
- PMCID: PMC7864217
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mser.2019.100522
Materials for blood brain barrier modeling in vitro
Abstract
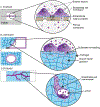
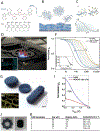
Brain homeostasis relies on the selective permeability property of the blood brain barrier (BBB). The BBB is formed by a continuous endothelium that regulates exchange between the blood stream and the brain. This physiological barrier also creates a challenge for the treatment of neurological diseases as it prevents most blood circulating drugs from entering into the brain. In vitro cell models aim to reproduce BBB functionality and predict the passage of active compounds through the barrier. In such systems, brain microvascular endothelial cells (BMECs) are cultured in contact with various biomaterial substrates. However, BMEC interactions with these biomaterials and their impact on BBB functions are poorly described in the literature. Here we review the most common materials used to culture BMECs and discuss their potential impact on BBB integrity in vitro. We investigate the biophysical properties of these biomaterials including stiffness, porosity and material degradability. We highlight a range of synthetic and natural materials and present three categories of cell culture dimensions: cell monolayers covering non-degradable materials (2D), cell monolayers covering degradable materials (2.5D) and vascularized systems developing into degradable materials (3D).
Keywords: Basement membrane; Biomaterial; Blood brain barrier; Extracellular matrix; Mechanotransduction; Organ-on-chip; Shear stress.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Potente M, Mäkinen T, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol 18 (2017) 477–494. - PubMed
-
- Abbott NJ, Patabendige AAK, Dolman DEM, Yusof SR, Begley DJ, Neurobiol. Dis 37 (2010) 13–25. - PubMed
-
- Cai Z, Qiao P-F, Wan C-Q, Cai M, Zhou N-K, Li Q, J. Alzheimer Dis 63 (2018) 1223–1234. - PubMed
-
- Kealy J, Greene C, Campbell M, Neurosci. Lett (2018). - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
