Chronic Cranial Windows for Long Term Multimodal Neurovascular Imaging in Mice
- PMID: 33551837
- PMCID: PMC7862556
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2020.612678
Chronic Cranial Windows for Long Term Multimodal Neurovascular Imaging in Mice
Abstract
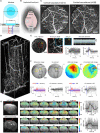
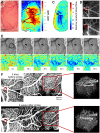
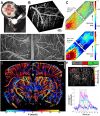
Chronic cranial windows allow for longitudinal brain imaging experiments in awake, behaving mice. Different imaging technologies have their unique advantages and combining multiple imaging modalities offers measurements of a wide spectrum of neuronal, glial, vascular, and metabolic parameters needed for comprehensive investigation of physiological and pathophysiological mechanisms. Here, we detail a suite of surgical techniques for installation of different cranial windows targeted for specific imaging technologies and their combination. Following these techniques and practices will yield higher experimental success and reproducibility of results.
Keywords: awake; chronic; imaging; mice; multimodal; neural; vascular.
Copyright © 2021 Kılıç, Desjardins, Tang, Thunemann, Sunil, Erdener, Postnov, Boas and Devor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Removable cranial windows for long-term imaging in awake mice.Nat Protoc. 2014 Nov;9(11):2515-2538. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2014.165. Epub 2014 Oct 2. Nat Protoc. 2014. PMID: 25275789 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic cranial window for photoacoustic imaging: a mini review.Vis Comput Ind Biomed Art. 2021 May 26;4(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s42492-021-00081-1. Vis Comput Ind Biomed Art. 2021. PMID: 34037873 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chronic Imaging of Mouse Brain: From Optical Systems to Functional Ultrasound.Curr Protoc Neurosci. 2020 Sep;93(1):e98. doi: 10.1002/cpns.98. Curr Protoc Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32584495 Free PMC article.
-
Head holder and cranial window design for sequential magnetic resonance imaging and optical imaging in awake mice.Front Neurosci. 2022 Aug 16;16:926828. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.926828. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36051645 Free PMC article.
-
Techniques for long-term multisite neuronal ensemble recordings in behaving animals.Methods. 2001 Oct;25(2):121-50. doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1231. Methods. 2001. PMID: 11812202 Review.
Cited by
-
Toward an integrative neurovascular framework for studying brain networks.Neurophotonics. 2022 Jul;9(3):032211. doi: 10.1117/1.NPh.9.3.032211. Epub 2022 Apr 7. Neurophotonics. 2022. PMID: 35434179 Free PMC article.
-
Capillaries susceptible to frequent stall dynamics revealed by comparing OCT and bessel-2PM measurements.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2025 Jun 25:271678X251353141. doi: 10.1177/0271678X251353141. Online ahead of print. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2025. PMID: 40562716 Free PMC article.
-
Baseline oxygen consumption decreases with cortical depth.PLoS Biol. 2022 Oct 27;20(10):e3001440. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3001440. eCollection 2022 Oct. PLoS Biol. 2022. PMID: 36301995 Free PMC article.
-
Optical coherence tomography guided automatic robotic craniotomy surgery platform.Biomed Opt Express. 2025 Jan 30;16(2):778-789. doi: 10.1364/BOE.549260. eCollection 2025 Feb 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2025. PMID: 39958837 Free PMC article.
-
Two-Photon Intravital Microscopy of Glioblastoma in a Murine Model.J Vis Exp. 2024 Mar 1;(205):10.3791/66304. doi: 10.3791/66304. J Vis Exp. 2024. PMID: 38497657 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

