Tracking Major Sources of Water Contamination Using Machine Learning
- PMID: 33552026
- PMCID: PMC7854693
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.616692
Tracking Major Sources of Water Contamination Using Machine Learning
Abstract
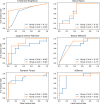
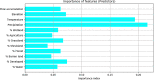
Current microbial source tracking techniques that rely on grab samples analyzed by individual endpoint assays are inadequate to explain microbial sources across space and time. Modeling and predicting host sources of microbial contamination could add a useful tool for watershed management. In this study, we tested and evaluated machine learning models to predict the major sources of microbial contamination in a watershed. We examined the relationship between microbial sources, land cover, weather, and hydrologic variables in a watershed in Northern California, United States. Six models, including K-nearest neighbors (KNN), Naïve Bayes, Support vector machine (SVM), simple neural network (NN), Random Forest, and XGBoost, were built to predict major microbial sources using land cover, weather and hydrologic variables. The results showed that these models successfully predicted microbial sources classified into two categories (human and non-human), with the average accuracy ranging from 69% (Naïve Bayes) to 88% (XGBoost). The area under curve (AUC) of the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) illustrated XGBoost had the best performance (average AUC = 0.88), followed by Random Forest (average AUC = 0.84), and KNN (average AUC = 0.74). The importance index obtained from Random Forest indicated that precipitation and temperature were the two most important factors to predict the dominant microbial source. These results suggest that machine learning models, particularly XGBoost, can predict the dominant sources of microbial contamination based on the relationship of microbial contaminants with daily weather and land cover, providing a powerful tool to understand microbial sources in water.
Keywords: XGBoost; fecal contamination; land use; machine learning; microbial source tracking; rainfall.
Copyright © 2021 Wu, Song, Dubinsky and Stewart.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Altman N. S. (1992). An introduction to kernel and nearest-neighbor nonparametric regression. Am. Statist. 46 175–185. 10.2307/2685209 - DOI
-
- Belanche L. A., Blanch A. R. (2011). “Statistical approaches for modeling in microbial source tracking,” in Microbial Source Tracking: Methods, Applications, and Case Studies, eds Harwood V. J., Hagedorn C., Blanch A. R. (Berlin: Springer; ), 207–227. 10.1007/978-1-4419-9386-1_9 - DOI
-
- Belanche-Muñoz L., Blanch A. R. (2008). Machine learning methods for microbial source tracking. Environ. Model. Softw. 23 741–750. 10.1016/j.envsoft.2007.09.013 - DOI
-
- Bishop C. M. (1995). Neural networks for pattern recognition. Oxford: Oxford university press.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources