The Clinical Significance and Potential Molecular Mechanism of PTTG1 in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 33552118
- PMCID: PMC7863988
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2020.583085
The Clinical Significance and Potential Molecular Mechanism of PTTG1 in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
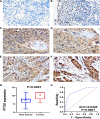
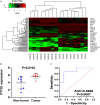
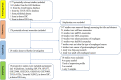
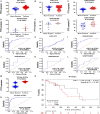
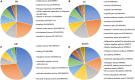
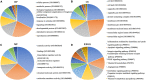
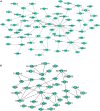
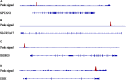
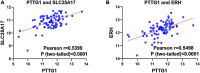
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) is the major histological type of esophageal cancers worldwide. Transcription factor PTTG1 was seen highly expressed in a variety of tumors and was related to the degree of tumor differentiation, invasion, and metastasis. However, the clinical significance of PTTG1 had yet to be verified, and the mechanism of abnormal PTTG1 expression in ESCC was not clear. In this study, the comprehensive analysis and evaluation of PTTG1 expression in ESCC were completed by synthesizing in-house immunohistochemistry (IHC), clinical sample tissue RNA-seq (in-house RNA-seq), public high-throughput data, and literature data. We also explored the possible signaling pathways and target genes of PTTG1 in ESCC by combining the target genes of PTTG1 (displayed by ChIP-seq), differentially expressed genes (DEGs) of ESCC, and PTTG1-related genes, revealing the potential molecular mechanism of PTTG1 in ESCC. In the present study, PTTG1 protein and mRNA expression levels in ESCC tissues were all significantly higher than in non-cancerous tissues. The pool standard mean difference (SMD) of the overall PTTG1 expression was 1.17 (95% CI: 0.72-1.62, P < 0.01), and the area under curve (AUC) of the summary receiver operating characteristic (SROC) was 0.86 (95% CI: 0.83-0.89). By combining the target genes displayed by ChIP-seq of PTTG1, DEGs of ESCC, and PTTG1-related genes, it was observed that PTTG1 may interact with these genes through chemokines and cytokine signaling pathways. By constructing a protein-protein interaction (PPI) network and combining ChIP-seq data, we obtained four PTTG1 potential target genes, SPTAN1, SLC25A17, IKBKB, and ERH. The gene expression of PTTG1 had a strong positive correlation with SLC25A17 and ERH, which suggested that PTTG1 might positively regulate the expression of these two genes. In summary, the high expression of PTTG1 may play an important role in the formation of ESCC. These roles may be completed by PTTG1 regulating the downstream target genes SLC25A17 and ERH.
Keywords: PTTG1; RNA sequencing; esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; tissue microarray; transcription factor.
Copyright © 2021 Chen, Zhou, Zhang, He, Huang, Dang, Yang, Liu, Fu, Mo, Tang, Li, Li, Yang, Ma, Yang and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

